Structural and Functional Insights into the C-terminal Fragment of Insecticidal Vip3A Toxin ofBacillus thuringiensis.
Jiang, K., Zhang, Y., Chen, Z., Wu, D., Cai, J., Gao, X.(2020) Toxins (Basel) 12
- PubMed: 32635593
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12070438
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
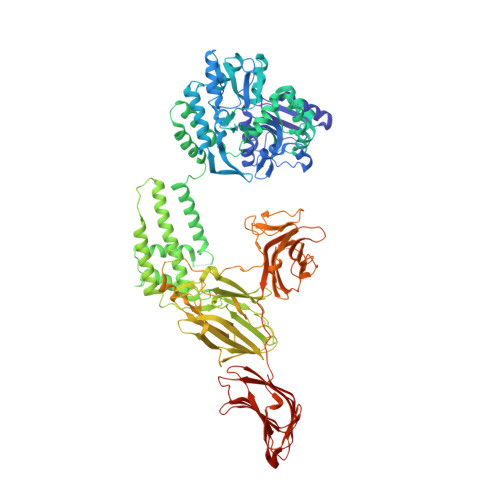
6VLS - PubMed Abstract:
The vegetative insecticidal proteins (Vips) secreted by Bacillus thuringiensis are regarded as the new generation of insecticidal toxins because they have different insecticidal properties compared with commonly applied insecticidal crystal proteins (Cry toxins). Vip3A toxin, representing the vast majority of Vips, has been used commercially in transgenic crops and bio-insecticides. However, the lack of both structural information on Vip3A and a clear understanding of its insecticidal mechanism at the molecular level limits its further development and broader application. Here we present the first crystal structure of the C-terminal fragment of Vip3A toxin (Vip3Aa11 200-789 ). Since all members of this insecticidal protein family are highly conserved, the structure of Vip3A provides unique insight into the general domain architecture and protein fold of the Vip3A family of insecticidal toxins. Our structural analysis reveals a four-domain organization, featuring a potential membrane insertion region, a receptor binding domain, and two potential glycan binding domains of Vip3A. In addition, cytotoxicity assays and insect bioassays show that the purified C-terminal fragment of Vip3Aa toxin alone have no insecticidal activity. Taken together, these findings provide insights into the mode of action of the Vip3A family of insecticidal toxins and will boost the development of Vip3A into more efficient bio-insecticides.
- State Key Laboratory of Microbial Technology, Shandong University, Qingdao 266237, China.
Organizational Affiliation: