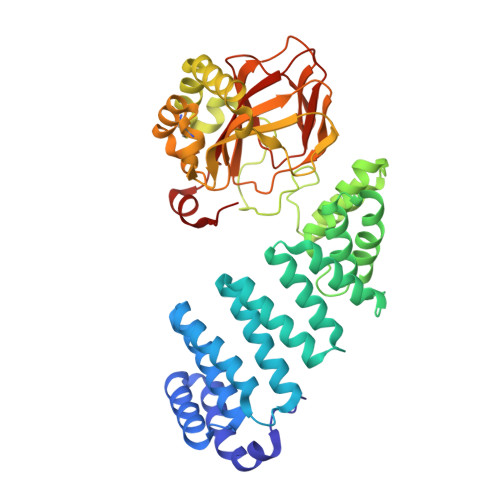
Aspartate/asparagine-beta-hydroxylase crystal structures reveal an unexpected epidermal growth factor-like domain substrate disulfide pattern.
Pfeffer, I., Brewitz, L., Krojer, T., Jensen, S.A., Kochan, G.T., Kershaw, N.J., Hewitson, K.S., McNeill, L.A., Kramer, H., Munzel, M., Hopkinson, R.J., Oppermann, U., Handford, P.A., McDonough, M.A., Schofield, C.J.(2019) Nat Commun 10: 4910-4910
- PubMed: 31659163
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12711-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5APA, 5JQY, 5JZ6, 5JZ8, 5JZA, 5JZU, 6RK9 - PubMed Abstract:
AspH is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane-anchored 2-oxoglutarate oxygenase whose C-terminal oxygenase and tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) domains present in the ER lumen. AspH catalyses hydroxylation of asparaginyl- and aspartyl-residues in epidermal growth factor-like domains (EGFDs). Here we report crystal structures of human AspH, with and without substrate, that reveal substantial conformational changes of the oxygenase and TPR domains during substrate binding. Fe(II)-binding by AspH is unusual, employing only two Fe(II)-binding ligands (His679/His725). Most EGFD structures adopt an established fold with a conserved Cys1-3, 2-4, 5-6 disulfide bonding pattern; an unexpected Cys3-4 disulfide bonding pattern is observed in AspH-EGFD substrate complexes, the catalytic relevance of which is supported by studies involving stable cyclic peptide substrate analogues and by effects of Ca(II) ions on activity. The results have implications for EGFD disulfide pattern processing in the ER and will enable medicinal chemistry efforts targeting human 2OG oxygenases.
- Chemistry Research Laboratory, University of Oxford, Mansfield Road, Oxford, OX1 3TA, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: