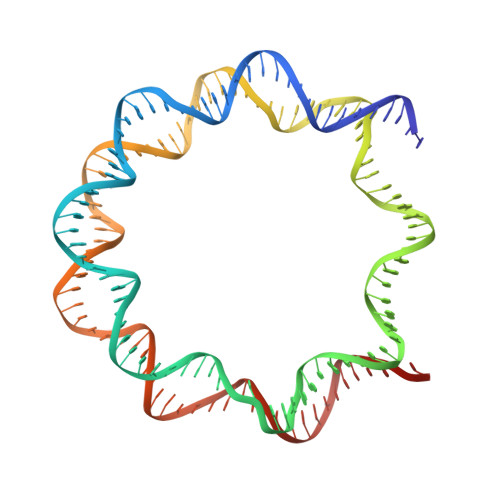
DNA damage detection in nucleosomes involves DNA register shifting.
Matsumoto, S., Cavadini, S., Bunker, R.D., Grand, R.S., Potenza, A., Rabl, J., Yamamoto, J., Schenk, A.D., Schubeler, D., Iwai, S., Sugasawa, K., Kurumizaka, H., Thoma, N.H.(2019) Nature 571: 79-84
- PubMed: 31142837
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1259-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6R8Y, 6R8Z, 6R90, 6R91, 6R92, 6R93, 6R94 - PubMed Abstract:
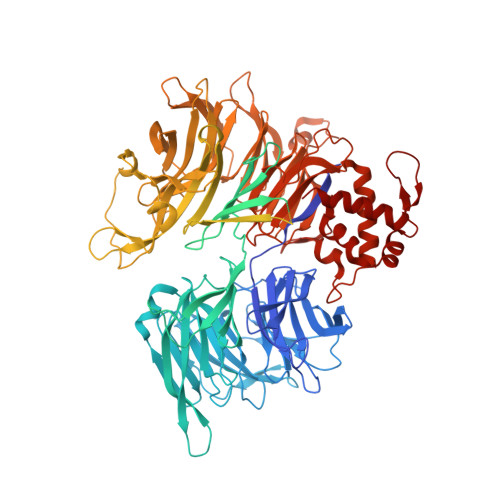
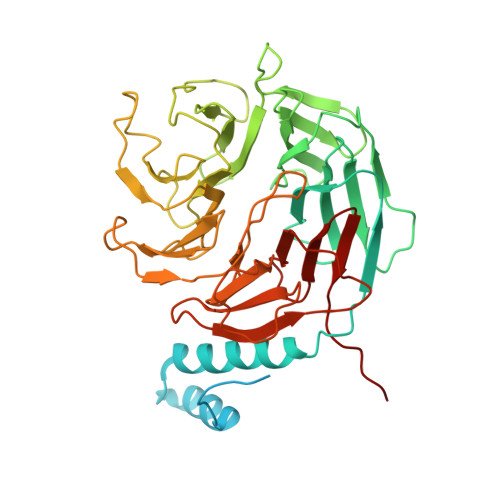
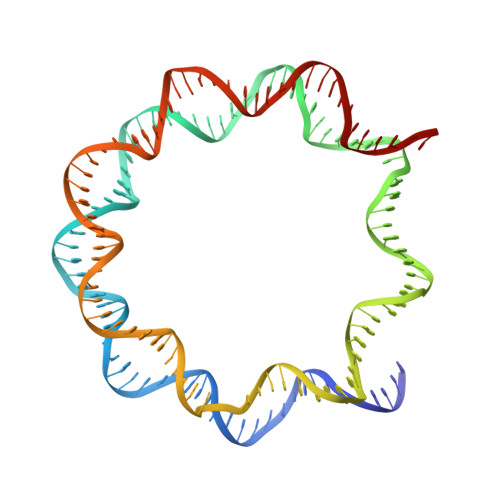
Access to DNA packaged in nucleosomes is critical for gene regulation, DNA replication and DNA repair. In humans, the UV-damaged DNA-binding protein (UV-DDB) complex detects UV-light-induced pyrimidine dimers throughout the genome; however, it remains unknown how these lesions are recognized in chromatin, in which nucleosomes restrict access to DNA. Here we report cryo-electron microscopy structures of UV-DDB bound to nucleosomes bearing a 6-4 pyrimidine-pyrimidone dimer or a DNA-damage mimic in various positions. We find that UV-DDB binds UV-damaged nucleosomes at lesions located in the solvent-facing minor groove without affecting the overall nucleosome architecture. In the case of buried lesions that face the histone core, UV-DDB changes the predominant translational register of the nucleosome and selectively binds the lesion in an accessible, exposed position. Our findings explain how UV-DDB detects occluded lesions in strongly positioned nucleosomes, and identify slide-assisted site exposure as a mechanism by which high-affinity DNA-binding proteins can access otherwise occluded sites in nucleosomal DNA.
- Friedrich Miescher Institute for Biomedical Research, Basel, Switzerland.
Organizational Affiliation: