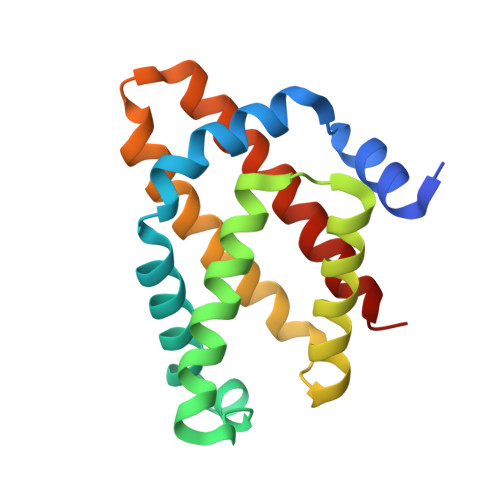
Disruption of the dimerization interface of the sensing domain in the dimeric heme-based oxygen sensorAfGcHK abolishes bacterial signal transduction.
Skalova, T., Lengalova, A., Dohnalek, J., Harlos, K., Mihalcin, P., Kolenko, P., Stranava, M., Blaha, J., Shimizu, T., Martinkova, M.(2020) J Biological Chem 295: 1587-1597
- PubMed: 31914416
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA119.011574
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6OTD - PubMed Abstract:
The heme-based oxygen sensor protein Af GcHK is a globin-coupled histidine kinase in the soil bacterium Anaeromyxobacter sp. Fw109-5. Its C-terminal functional domain exhibits autophosphorylation activity induced by oxygen binding to the heme-Fe(II) complex located in the oxygen-sensing N-terminal globin domain. A detailed understanding of the signal transduction mechanisms in heme-containing sensor proteins remains elusive. Here, we investigated the role of the globin domain's dimerization interface in signal transduction in Af GcHK. We present a crystal structure of a monomeric imidazole-bound Af GcHK globin domain at 1.8 Å resolution, revealing that the helices of the WT globin dimer are under tension and suggesting that Tyr-15 plays a role in both this tension and the globin domain's dimerization. Biophysical experiments revealed that whereas the isolated WT globin domain is dimeric in solution, the Y15A and Y15G variants in which Tyr-15 is replaced with Ala or Gly, respectively, are monomeric. Additionally, we found that although the dimerization of the full-length protein is preserved via the kinase domain dimerization interface in all variants, full-length Af GcHK variants bearing the Y15A or Y15G substitutions lack enzymatic activity. The combined structural and biophysical results presented here indicate that Tyr-15 plays a key role in the dimerization of the globin domain of Af GcHK and that globin domain dimerization is essential for internal signal transduction and autophosphorylation in this protein. These findings provide critical insights into the signal transduction mechanism of the histidine kinase Af GcHK from Anaeromyxobacter .
- Institute of Biotechnology of the Czech Academy of Sciences, v.v.i., Biocev, Vestec, 252 50 Czech Republic.
Organizational Affiliation: