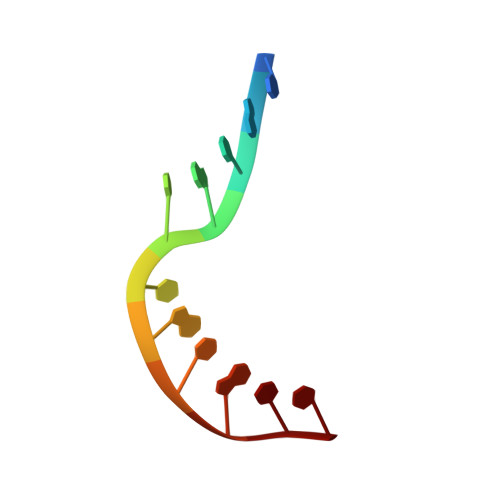
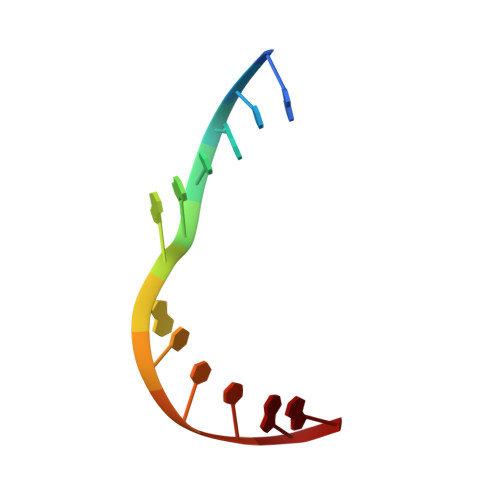
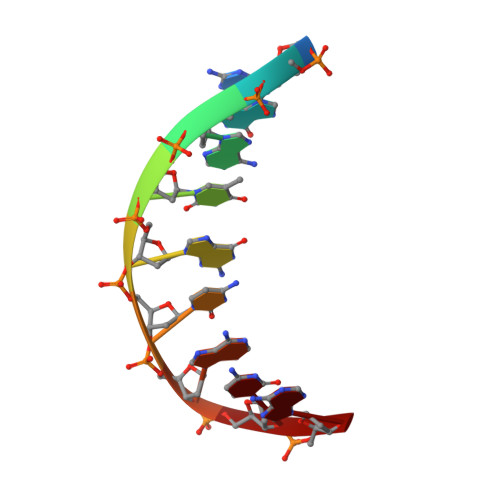
Self-Assembly of a 3D DNA Crystal Structure with Rationally Designed Six-Fold Symmetry.
Zhang, F., Simmons, C.R., Gates, J., Liu, Y., Yan, H.(2018) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 57: 12504-12507
- PubMed: 30066355
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201807223
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6DKL - PubMed Abstract:
Programming self-assembled designer DNA crystals with various lattices and functions is one of the most important goals for nanofabrication using nucleic acids. The resulting porous materials possess atomic precision for several potential applications that rely on crystalline lattices and cavities. Herein, we present a rationally designed and self-assembled 3D DNA crystal lattice with hexagonal symmetry. In our design, two 21-base oligonucleotides are used to form a duplex motif that further assembles into a 3D array. The interactions between the strands are programmed using Watson-Crick base-pairing. The six-fold symmetry, as well as the chirality, is directed by the Holliday junctions formed between the duplex motifs. The rationally designed DNA crystal provides a new avenue that could create self-assembled macromolecular 3D crystalline lattices with atomic precision. In addition, the structure contains a highly organized array of well-defined cavities that are suitable for future applications with immobilized guests.
- School of Molecular Sciences and Biodesign Institution, Arizona State University, 1001 S McAllister Ave, Tempe, AZ, 85281, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: