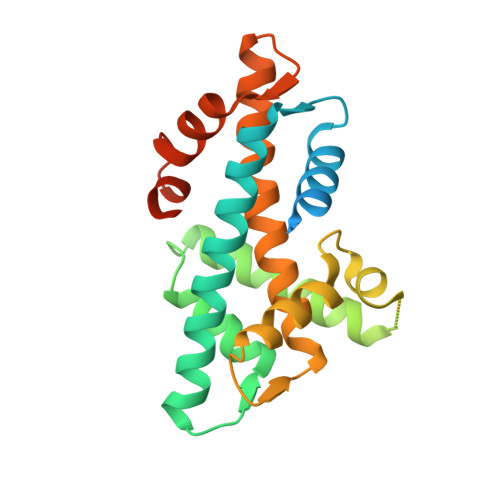
Crystal structure of the histone heterodimer containing histone variant H2A.Bbd.
Dai, L., Xie, X., Zhou, Z.(2018) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503: 1786-1791
- PubMed: 30064909
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.07.114
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6A7U - PubMed Abstract:
H2A.Bbd, the most divergent histone variant among all known H2A type histones, is involved in gene transcription, spermiogenesis, DNA replication and RNA splicing. Incorporation of H2A.Bbd-H2B dimer, a fundamental unit of H2A.Bbd nucleosome, modulate structures of nucleosome or chromatin, but the underlying mechanism remains elusive. Here we determined a crystal structure of H2A.Bbd-H2B dimer at 2.6 Å resolution. Although the H2A.Bbd-H2B dimer structure largely resembles that of H2A-H2B, substitution of H2A αC helix residues by H2A.Bbd counterparts lead to the transition of a long αC-helix to the short 3 10 -helix, likely owing to the rearrangement of the hydrogen-bond network. Moreover, structural comparison revealed a strikingly altered electrostatic potential surface for H2A.Bbd-H2B dimer displaying a diminished DNA binding capability. Our study provides the first high-resolution structure of histone variant H2A.Bbd and shed a light on biological function of H2A.Bbd.
- University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026, China; National Laboratory of Biomacromolecules, CAS Center for Excellence in Biomacromolecules, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100101, China.
Organizational Affiliation: