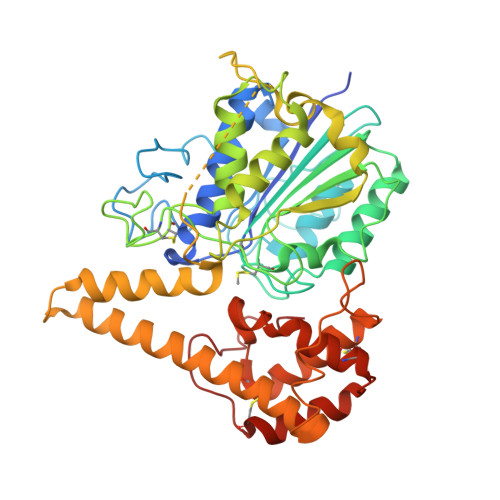
Crystal Structure of Plant Legumain Reveals a Unique Two-Chain State with pH-Dependent Activity Regulation.
Zauner, F.B., Dall, E., Regl, C., Grassi, L., Huber, C.G., Cabrele, C., Brandstetter, H.(2018) Plant Cell 30: 686-699
- PubMed: 29453229
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00963
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5NIJ - PubMed Abstract:
The vacuolar cysteine protease legumain can cleave and selectively rebuild peptide bonds, thereby vastly expanding the sequential repertoire of biomolecules. In this context, plant legumains have recently attracted particular interest. Furthermore, legumains have important roles in many physiological processes, including programmed cell death. Their efficient peptide bond ligase activity has gained tremendous interest in the design of cyclic peptides for drug design. However, the mechanistic understanding of these dual activities is incomplete and partly conflicting. Here, we present the crystal structure of a plant legumain, Arabidopsis thaliana isoform-γ (AtLEGγ). Employing a conserved legumain fold, the plant legumain AtLEGγ revealed unique mechanisms of autoactivation, including a plant-specific two-chain activation state, which remains conformationally stable at neutral pH, which is a prerequisite for full ligase activity and survival in different cell compartments. The charge distribution around the α6-helix mediates the pH-dependent dimerization and serves as a gatekeeper for the active site, thus regulating its protease and ligase activity.
- Department of Molecular Biology and Christian Doppler Laboratory for Biosimilar Research, University of Salzburg, A-5020 Salzburg, Austria.
Organizational Affiliation: