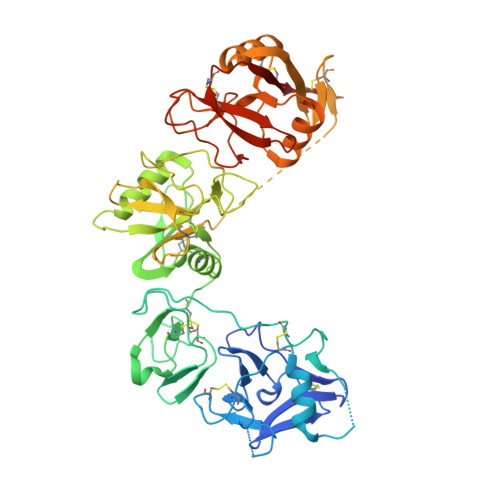
Crystal structures of the ligand-binding region of uPARAP: effect of calcium ion binding
Yuan, C., Jurgensen, H.J., Engelholm, L.H., Li, R., Liu, M., Jiang, L., Luo, Z., Behrendt, N., Huang, M.(2016) Biochem J 473: 2359-2368
- PubMed: 27247422
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20160276
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5E4K, 5EW6 - PubMed Abstract:
The proteins of the mannose receptor (MR) family share a common domain organization and have a broad range of biological functions. Urokinase plasminogen activator receptor-associated protein (uPARAP) (or Endo180) is a member of this family and plays an important role in extracellular matrix remodelling through interaction with its ligands, including collagens and urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR). We report the crystal structures of the first four domains of uPARAP (also named the ligand-binding region, LBR) at pH 7.4 in Ca(2+)-bound and Ca(2+)-free forms. The first domain (cysteine-rich or CysR domain) folds into a new and unique conformation different from the β-trefoil fold of typical CysR domains. The so-called long loop regions (LLRs) of the C-type lectin-like domain (CTLD) 1 and 2 (the third and fourth domain) mediate the direct contacts between these domains. These LLRs undergo a Ca(2+)-dependent conformational change, and this is likely to be the key structural determinant affecting the overall conformation of uPARAP. Our results provide a molecular mechanism to support the structural flexibility of uPARAP, and shed light on the structural flexibility of other members of the MR family.
- State Key Laboratory of Structural Chemistry, Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Fuzhou 350002, China College of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou 350108, China.
Organizational Affiliation: