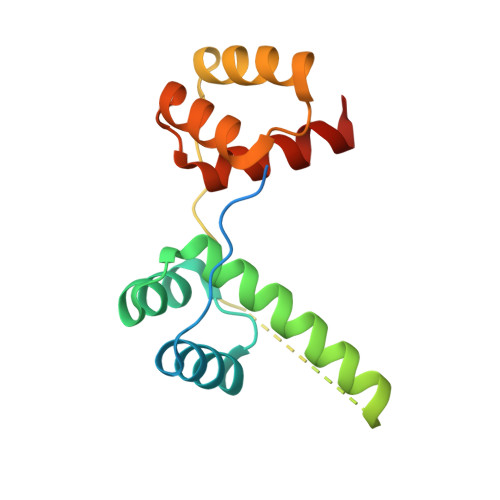
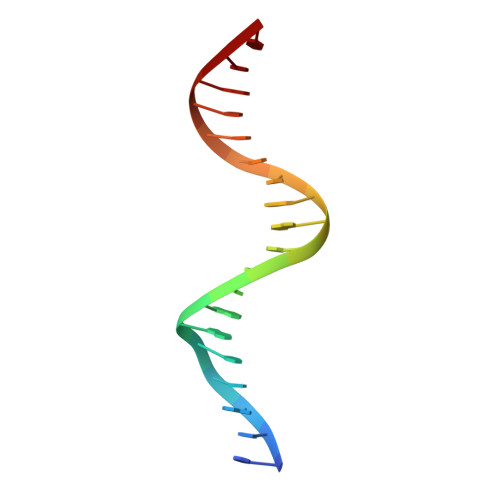
Structural basis for multiple gene regulation by human DUX4.
Li, Y., Wu, B., Liu, H., Gao, Y., Yang, C., Chen, X., Zhang, J., Chen, Y., Gu, Y., Li, J., Ma, J., Gan, J.(2018) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 505: 1161-1167
- PubMed: 30322619
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.10.056
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5Z6Z, 5ZFW, 5ZFY, 5ZFZ - PubMed Abstract:
DUX4 plays critical role in the molecular pathogenesis of the neuromuscular disorder facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy and acute lymphoblastic leukemia in humans. As a master transcription regulator, DUX4 can also bind the promoters and activate the transcription of hundreds ZGA-associated genes. Here we report on the structural and biochemical studies of DUX4 double homeodomains (DUX4-DH), representing the only structures contain both homeodomain 1 (HD1) and homeodomain 2 (HD2). HD1 and HD2 adopt classical homeobox fold; via the helix inserted into the major groove and the N-terminal extended loop inserted into the minor groove, HD1 and HD2 recognize the box1 (5'-TAA-3') and box2 (5'-TGA-3') nucleotides of the consensus sequence, respectively. Among the box1 and box2 linking nucleotides (CCTAA), the two adenine residues are reported to be highly conserved; however, they are not directly recognized by DUX4-DH in the structures. Besides different nucleotides, our ITC analysis indicated that DUX4-DH can also tolerate various changes in the linker length. Our studies not only revealed the basis for target DNA recognition by DUX4, but also advanced our understanding on multiple gene activation by DUX4.
- State Key Laboratory of Genetic Engineering, Collaborative Innovation Center of Genetics and Development, Department of Physiology and Biophysics, School of Life Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438, China.
Organizational Affiliation: