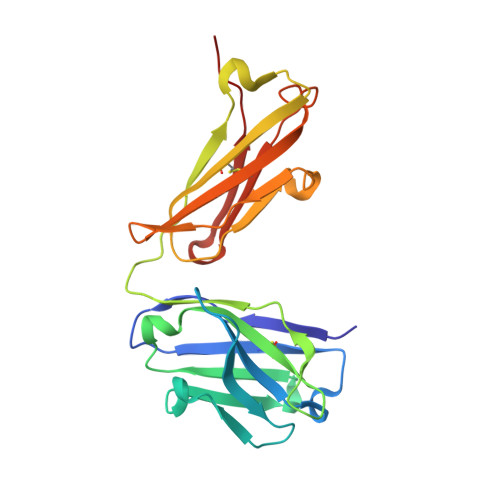
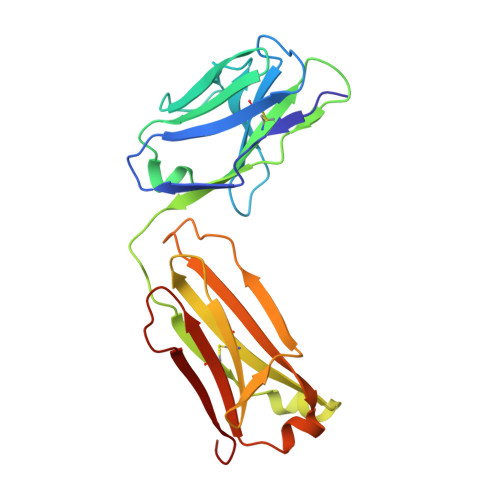
Crystal structure, epitope, and functional impact of an antibody against a superactive FVIIa provide insights into allosteric mechanism.
Jiang, L.G., Xie, X., Li, J., Persson, E., Huang, M.D.(2019) Res Pract Thromb Haemost 3: 412-419
- PubMed: 31294329
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/rth2.12211
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5YUP - PubMed Abstract:
Blood coagulation factor VIIa (FVIIa) plays its critical physiological role in the initiation of hemostasis. Even so, recombinant FVIIa is successfully used as a bypassing agent for factor VIII or IX in the treatment of bleeds in patients with severe hemophilia with inhibitors. To investigate the utility of more potent FVIIa variants with enhanced intrinsic activity, molecules such as V21D/E154V/M156Q-FVIIa (FVIIa DVQ ) were designed. Surface plasmon resonance was used to characterize the binding of mAb4F5 to FVIIa DVQ and related variants. X-ray crystallography was used to determine the structure of the Fab fragment of mAb4F5 (Fab4F5). Molecular docking and small angle X-ray scattering led to a model of FVIIa DVQ :Fab4F5 complex. The binding experiments, functional effects on FVIIa DVQ and structure of mAb4F5 (originally intended for quantification of FVIIa DVQ in samples containing FVII(a)) pinpointed the epitope (crucial role for residue Asp21) and shed light on the role of the N-terminus of the protease domain in FVIIa allostery. The potential antigen-combining sites are composed of 1 hydrophobic and 1 negatively charged pocket formed by 6 complementarity-determining region (CDR) loops. Structural analysis of Fab4F5 shows that the epitope interacts with the periphery of the hydrophobic pocket and provides insights into the molecular basis of mAb4F5 recognition and tight binding of FVIIa DVQ . The binary complex explains and supports the selectivity and functional consequences of Fab4F5 association with FVIIa DVQ and illustrates the potentially unique antigenicity of this FVIIa variant. This will be useful in the design of less immunogenic variants.
- College of Chemistry National & Local Joint Biomedical Engineering Research Center on Photodynamic Technologies Fuzhou University Fuzhou China.
Organizational Affiliation: