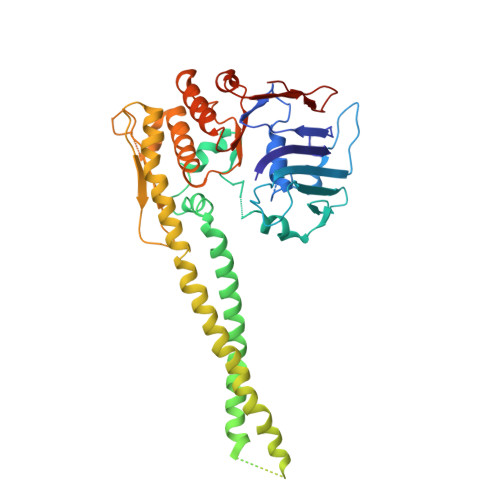
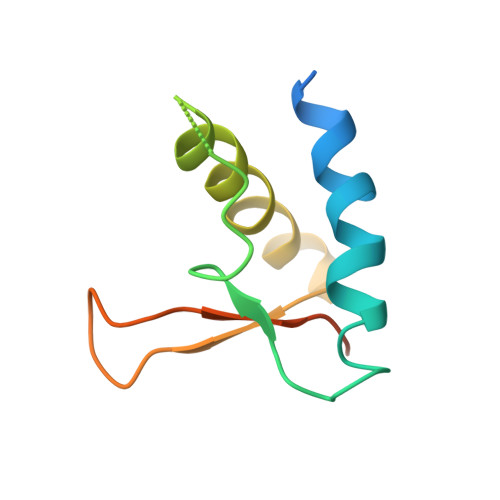
Structure of Full-Length SMC and Rearrangements Required for Chromosome Organization
Diebold-Durand, M.L., Lee, H., Ruiz Avila, L.B., Noh, H., Shin, H.C., Im, H., Bock, F.P., Burmann, F., Durand, A., Basfeld, A., Ham, S., Basquin, J., Oh, B.-H., Gruber, S.(2017) Mol Cell 67: 334-347.e5
- PubMed: 28689660
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.06.010
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5NMO, 5NNV, 5XEI, 5XG2, 5XG3, 5XNS - PubMed Abstract:
Multi-subunit SMC complexes control chromosome superstructure and promote chromosome disjunction, conceivably by actively translocating along DNA double helices. SMC subunits comprise an ABC ATPase "head" and a "hinge" dimerization domain connected by a 49 nm coiled-coil "arm." The heads undergo ATP-dependent engagement and disengagement to drive SMC action on the chromosome. Here, we elucidate the architecture of prokaryotic Smc dimers by high-throughput cysteine cross-linking and crystallography. Co-alignment of the Smc arms tightly closes the interarm space and misaligns the Smc head domains at the end of the rod by close apposition of their ABC signature motifs. Sandwiching of ATP molecules between Smc heads requires them to substantially tilt and translate relative to each other, thereby opening up the Smc arms. We show that this mechanochemical gating reaction regulates chromosome targeting and propose a mechanism for DNA translocation based on the merging of DNA loops upon closure of Smc arms.
- Chromosome Organisation and Dynamics, Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry, Am Klopferspitz 18, 82152 Martinsried, Germany; Department of Fundamental Microbiology, University of Lausanne, Bâtiment Biophore, 1015 Lausanne, Switzerland.
Organizational Affiliation: