Structural mechanism for nucleotide-driven remodeling of the AAA-ATPase unfoldase in the activated human 26S proteasome.
Zhu, Y., Wang, W.L., Yu, D., Ouyang, Q., Lu, Y., Mao, Y.(2018) Nat Commun 9: 1360-1360
- PubMed: 29636472
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03785-w
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5VFO, 5VFP, 5VFQ, 5VFR, 5VFS, 5VFT, 5VFU - PubMed Abstract:
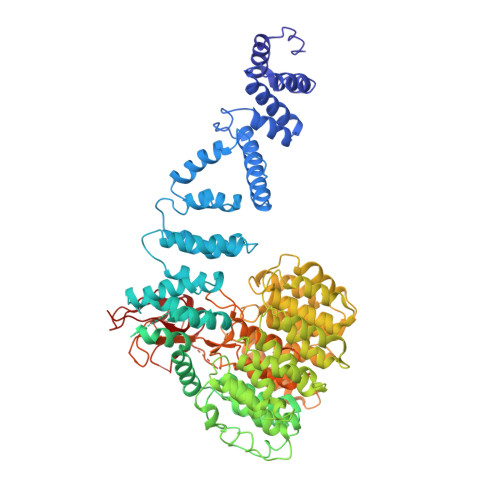
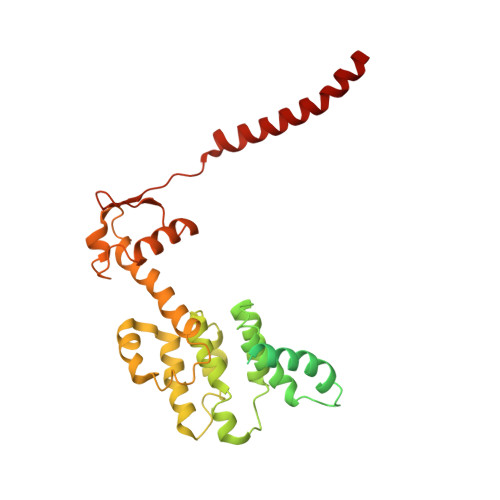
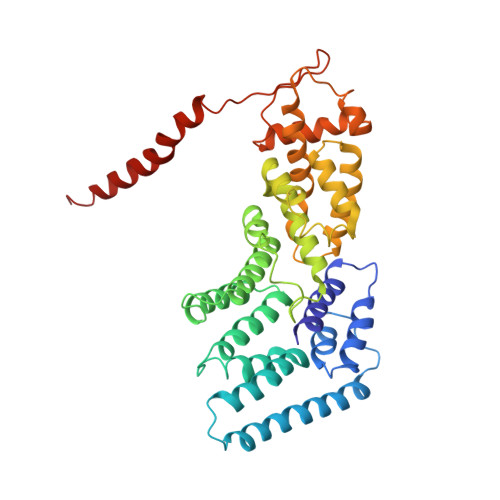
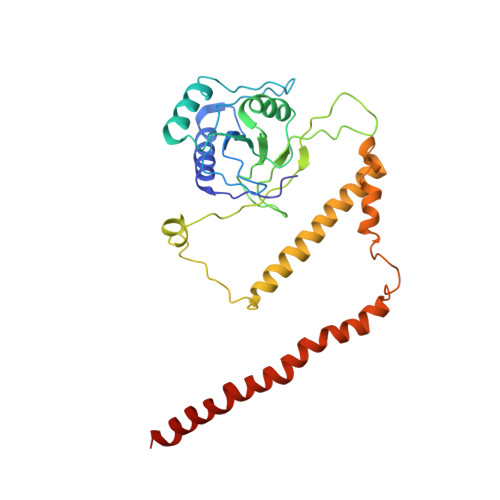
The proteasome is a sophisticated ATP-dependent molecular machine responsible for protein degradation in all known eukaryotic cells. It remains elusive how conformational changes of the AAA-ATPase unfoldase in the regulatory particle (RP) control the gating of the substrate-translocation channel leading to the proteolytic chamber of the core particle (CP). Here we report three alternative states of the ATP-γ-S-bound human proteasome, in which the CP gates are asymmetrically open, visualized by cryo-EM at near-atomic resolutions. At least four nucleotides are bound to the AAA-ATPase ring in these open-gate states. Variation in nucleotide binding gives rise to an axial movement of the pore loops narrowing the substrate-translation channel, which exhibit remarkable structural transitions between the spiral-staircase and saddle-shaped-circle topologies. Gate opening in the CP is thus regulated by nucleotide-driven conformational changes of the AAA-ATPase unfoldase. These findings demonstrate an elegant mechanism of allosteric coordination among sub-machines within the human proteasome holoenzyme.
- Center for Quantitative Biology, Peking University, Beijing, 100871, China.
Organizational Affiliation: