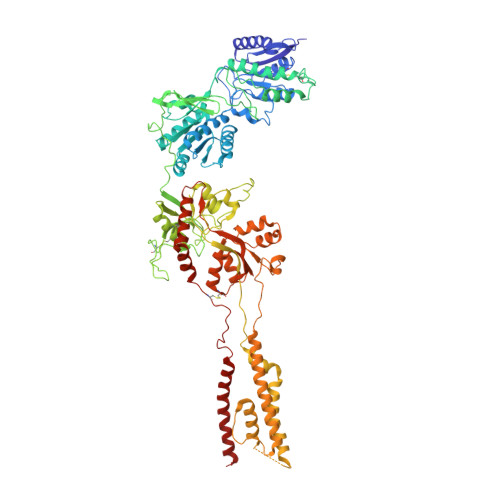
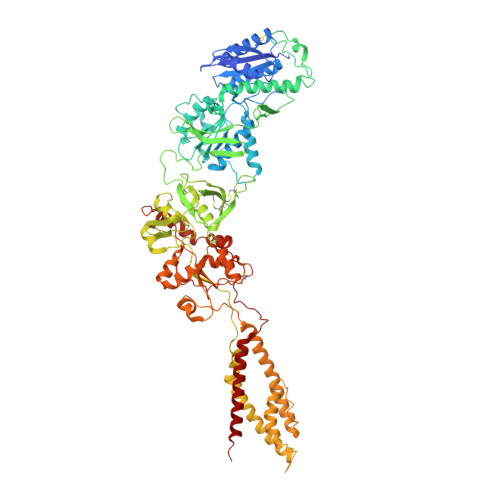
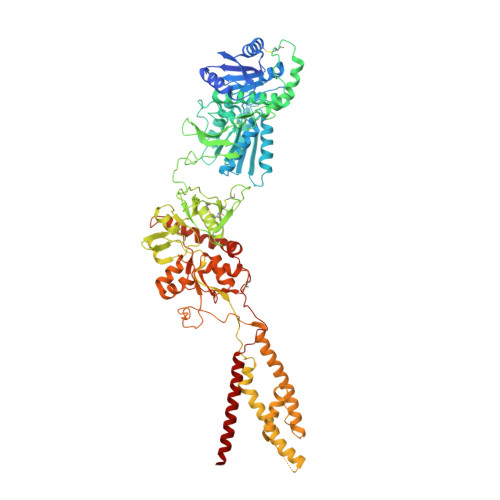
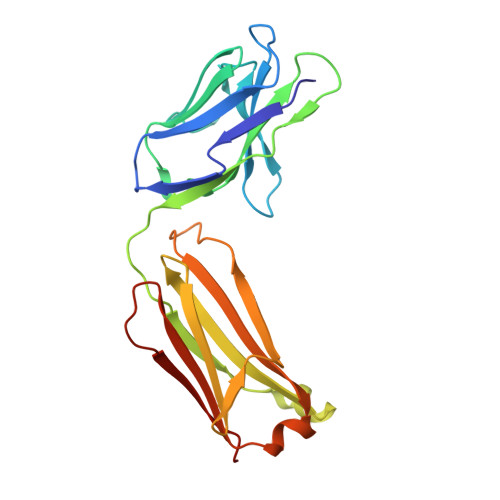
Cryo-EM structures of the triheteromeric NMDA receptor and its allosteric modulation.
Lu, W., Du, J., Goehring, A., Gouaux, E.(2017) Science 355
- PubMed: 28232581
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aal3729
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5UOW, 5UP2 - PubMed Abstract:
N -methyl-d-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) are heterotetrameric ion channels assembled as diheteromeric or triheteromeric complexes. Here, we report structures of the triheteromeric GluN1/GluN2A/GluN2B receptor in the absence or presence of the GluN2B-specific allosteric modulator Ro 25-6981 (Ro), determined by cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM). In the absence of Ro, the GluN2A and GluN2B amino-terminal domains (ATDs) adopt "closed" and "open" clefts, respectively. Upon binding Ro, the GluN2B ATD clamshell transitions from an open to a closed conformation. Consistent with a predominance of the GluN2A subunit in ion channel gating, the GluN2A subunit interacts more extensively with GluN1 subunits throughout the receptor, in comparison with the GluN2B subunit. Differences in the conformation of the pseudo-2-fold-related GluN1 subunits further reflect receptor asymmetry. The triheteromeric NMDAR structures provide the first view of the most common NMDA receptor assembly and show how incorporation of two different GluN2 subunits modifies receptor symmetry and subunit interactions, allowing each subunit to uniquely influence receptor structure and function, thus increasing receptor complexity.
- Vollum Institute, Oregon Health and Science University, 3181 Southwest Sam Jackson Park Road, Portland, OR 97239, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: