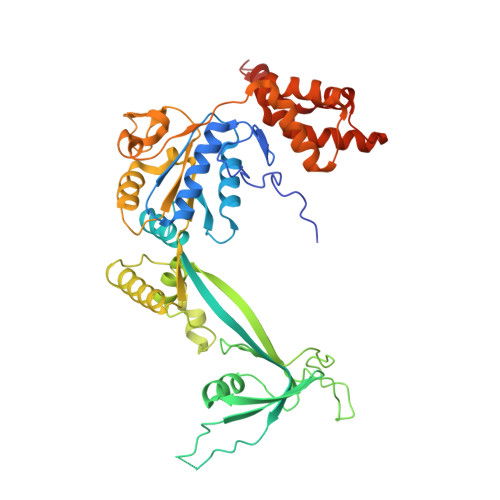
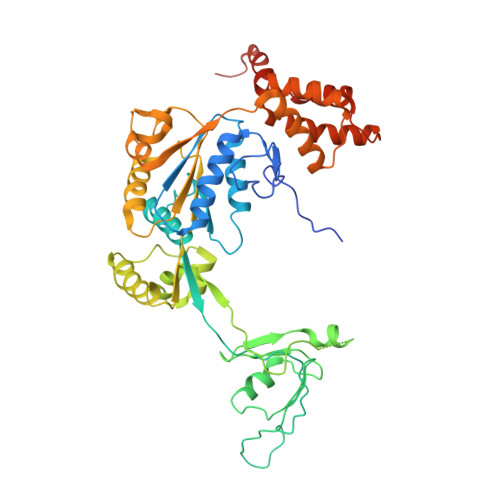
Cryo-EM structures of the human INO80 chromatin-remodeling complex.
Aramayo, R.J., Willhoft, O., Ayala, R., Bythell-Douglas, R., Wigley, D.B., Zhang, X.(2018) Nat Struct Mol Biol 25: 37-44
- PubMed: 29323271
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-017-0003-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5OAF - PubMed Abstract:
Access to chromatin for processes such as transcription and DNA repair requires the sliding of nucleosomes along DNA. This process is aided by chromatin-remodeling complexes, such as the multisubunit INO80 chromatin-remodeling complex. Here we present cryo-EM structures of the active core complex of human INO80 at 9.6 Å, with portions at 4.1-Å resolution, and reconstructions of combinations of subunits. Together, these structures reveal the architecture of the INO80 complex, including Ino80 and actin-related proteins, which is assembled around a single RUVBL1 (Tip49a) and RUVBL2 (Tip49b) AAA+ heterohexamer. An unusual spoked-wheel structural domain of the Ino80 subunit is engulfed by this heterohexamer; both, in combination, form the core of the complex. We also identify a cleft in RUVBL1 and RUVBL2, which forms a major interaction site for partner proteins and probably communicates these interactions to its nucleotide-binding sites.
- Section of Structural Biology, Department of Medicine, Imperial College London, London, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: