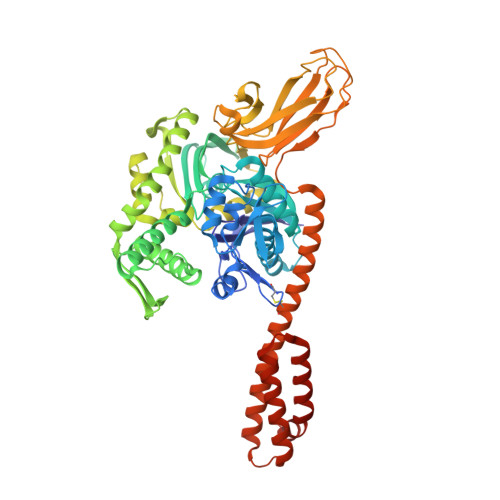
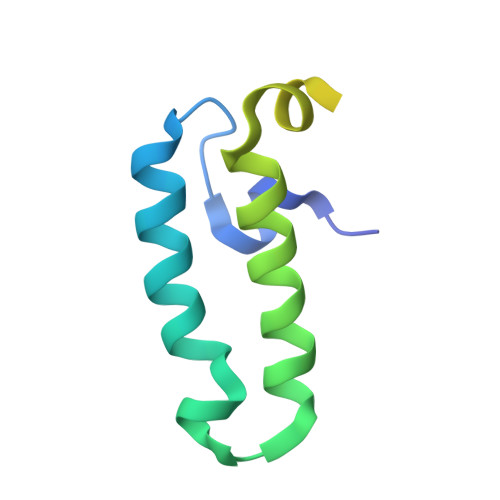
Molecular Mechanism of J-Domain-Triggered ATP Hydrolysis by Hsp70 Chaperones.
Kityk, R., Kopp, J., Mayer, M.P.(2018) Mol Cell 69: 227-237.e4
- PubMed: 29290615
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.12.003
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5NRO - PubMed Abstract:
Efficient targeting of Hsp70 chaperones to substrate proteins depends on J-domain cochaperones, which in synergism with substrates trigger ATP hydrolysis in Hsp70s and concomitant substrate trapping. We present the crystal structure of the J-domain of Escherichia coli DnaJ in complex with the E. coli Hsp70 DnaK. The J-domain interacts not only with DnaK's nucleotide-binding domain (NBD) but also with its substrate-binding domain (SBD) and packs against the highly conserved interdomain linker. Mutational replacement of contacts between J-domain and SBD strongly reduces the ability of substrates to stimulate ATP hydrolysis in the presence of DnaJ and compromises viability at heat shock temperatures. Our data demonstrate that the J-domain and the substrate do not deliver completely independent signals for ATP hydrolysis, but the J-domain, in addition to its direct influence on Hsp70s catalytic center, makes Hsp70 more responsive for the hydrolysis-inducing signal of the substrate, resulting in efficient substrate trapping.
- Center for Molecular Biology of Heidelberg University (ZMBH), DKFZ-ZMBH Alliance, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: