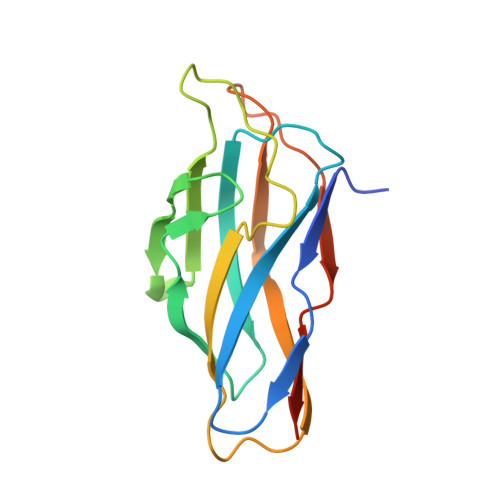
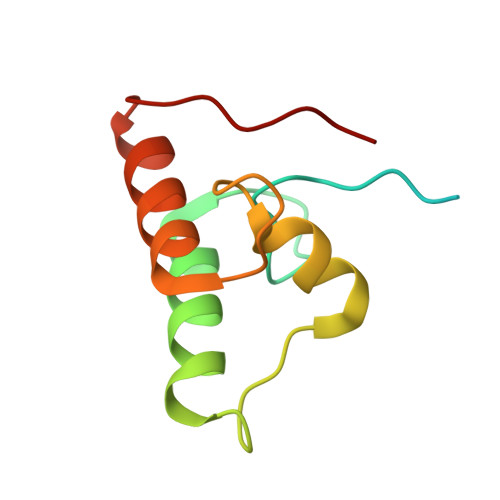
Assembly of Ruminococcus flavefaciens cellulosome revealed by structures of two cohesin-dockerin complexes.
Bule, P., Alves, V.D., Israeli-Ruimy, V., Carvalho, A.L., Ferreira, L.M., Smith, S.P., Gilbert, H.J., Najmudin, S., Bayer, E.A., Fontes, C.M.(2017) Sci Rep 7: 759-759
- PubMed: 28389644
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00919-w
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5M2O, 5M2S - PubMed Abstract:
Cellulosomes are sophisticated multi-enzymatic nanomachines produced by anaerobes to effectively deconstruct plant structural carbohydrates. Cellulosome assembly involves the binding of enzyme-borne dockerins (Doc) to repeated cohesin (Coh) modules located in a non-catalytic scaffoldin. Docs appended to cellulosomal enzymes generally present two similar Coh-binding interfaces supporting a dual-binding mode, which may confer increased positional adjustment of the different complex components. Ruminococcus flavefaciens' cellulosome is assembled from a repertoire of 223 Doc-containing proteins classified into 6 groups. Recent studies revealed that Docs of groups 3 and 6 are recruited to the cellulosome via a single-binding mode mechanism with an adaptor scaffoldin. To investigate the extent to which the single-binding mode contributes to the assembly of R. flavefaciens cellulosome, the structures of two group 1 Docs bound to Cohs of primary (ScaA) and adaptor (ScaB) scaffoldins were solved. The data revealed that group 1 Docs display a conserved mechanism of Coh recognition involving a single-binding mode. Therefore, in contrast to all cellulosomes described to date, the assembly of R. flavefaciens cellulosome involves single but not dual-binding mode Docs. Thus, this work reveals a novel mechanism of cellulosome assembly and challenges the ubiquitous implication of the dual-binding mode in the acquisition of cellulosome flexibility.
- CIISA - Faculdade de Medicina Veterinária, ULisboa, Pólo Universitário do Alto da Ajuda, Avenida da Universidade Técnica, 1300-477, Lisboa, Portugal.
Organizational Affiliation: