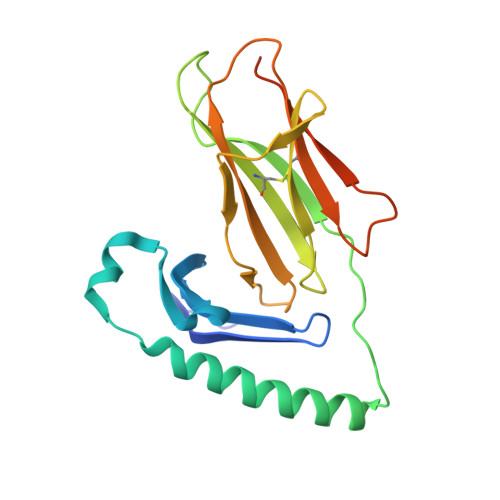
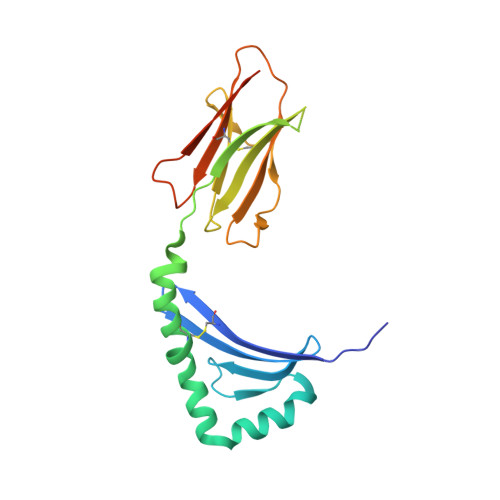
Unraveling the structural basis for the unusually rich association of human leukocyte antigen DQ2.5 with class-II-associated invariant chain peptides.
Nguyen, T.B., Jayaraman, P., Bergseng, E., Madhusudhan, M.S., Kim, C.Y., Sollid, L.M.(2017) J Biological Chem 292: 9218-9228
- PubMed: 28364043
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.785139
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5KSU, 5KSV - PubMed Abstract:
Human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DQ2.5 ( DQA1 * 05/DQB1 * 02 ) is a class-II major histocompatibility complex protein associated with both type 1 diabetes and celiac disease. One unusual feature of DQ2.5 is its high class-II-associated invariant chain peptide (CLIP) content. Moreover, HLA-DQ2.5 preferentially binds the non-canonical CLIP2 over the canonical CLIP1. To better understand the structural basis of HLA-DQ2.5's unusual CLIP association characteristics, better insight into the HLA-DQ2.5·CLIP complex structures is required. To this end, we determined the X-ray crystal structure of the HLA-DQ2.5· CLIP1 and HLA-DQ2.5·CLIP2 complexes at 2.73 and 2.20 Å, respectively. We found that HLA-DQ2.5 has an unusually large P4 pocket and a positively charged peptide-binding groove that together promote preferential binding of CLIP2 over CLIP1. An α9-α22-α24-α31-β86-β90 hydrogen bond network located at the bottom of the peptide-binding groove, spanning from the P1 to P4 pockets, renders the residues in this region relatively immobile. This hydrogen bond network, along with a deletion mutation at α53, may lead to HLA-DM insensitivity in HLA-DQ2.5. A molecular dynamics simulation experiment reported here and recent biochemical studies by others support this hypothesis. The diminished HLA-DM sensitivity is the likely reason for the CLIP-rich phenotype of HLA-DQ2.5.
- the Bioinformatics Institute, Singapore 138671, Singapore.
Organizational Affiliation: