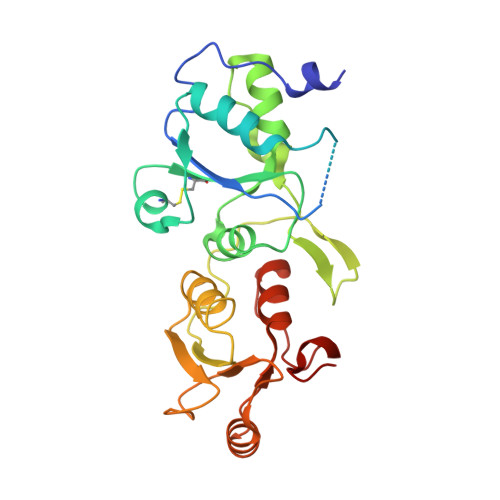
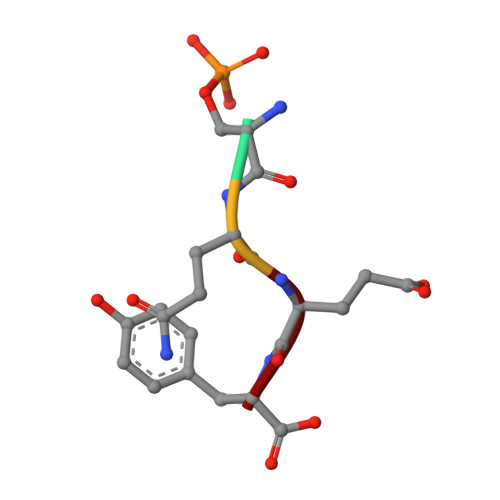
ATM Localization and Heterochromatin Repair Depend on Direct Interaction of the 53BP1-BRCT2 Domain with gamma H2AX.
Baldock, R.A., Day, M., Wilkinson, O.J., Cloney, R., Jeggo, P.A., Oliver, A.W., Watts, F.Z., Pearl, L.H.(2015) Cell Rep 13: 2081-2089
- PubMed: 26628370
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2015.10.074
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5ECG - PubMed Abstract:
53BP1 plays multiple roles in mammalian DNA damage repair, mediating pathway choice and facilitating DNA double-strand break repair in heterochromatin. Although it possesses a C-terminal BRCT2 domain, commonly involved in phospho-peptide binding in other proteins, initial recruitment of 53BP1 to sites of DNA damage depends on interaction with histone post-translational modifications--H4K20me2 and H2AK13/K15ub--downstream of the early γH2AX phosphorylation mark of DNA damage. We now show that, contrary to current models, the 53BP1-BRCT2 domain binds γH2AX directly, providing a third post-translational mark regulating 53BP1 function. We find that the interaction of 53BP1 with γH2AX is required for sustaining the 53BP1-dependent focal concentration of activated ATM that facilitates repair of DNA double-strand breaks in heterochromatin in G1.
- Genome Damage and Stability Centre, School of Life Sciences, University of Sussex, Falmer, Brighton BN1 9RQ, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: