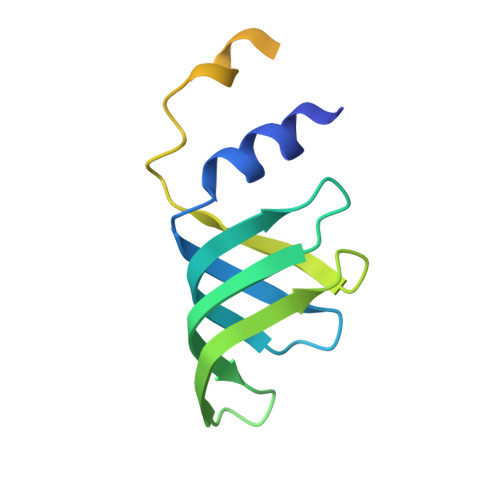
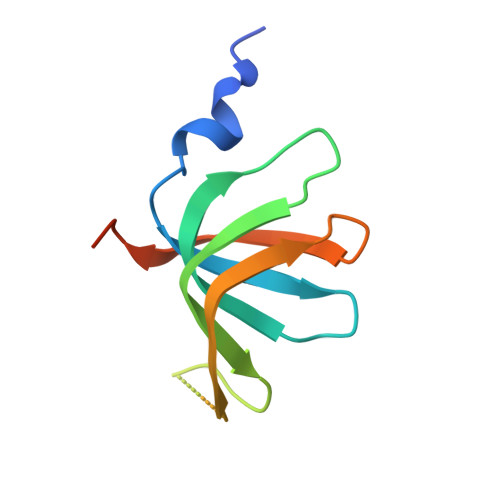
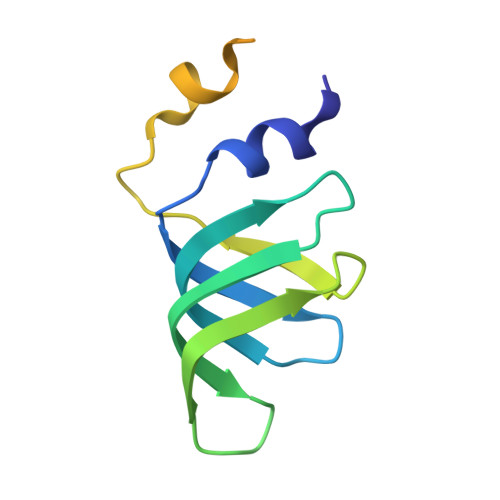
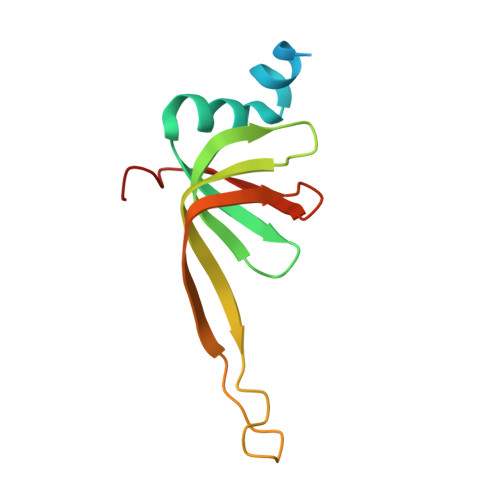
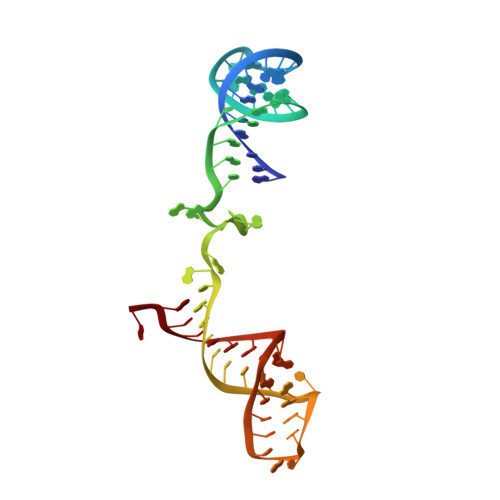
Structure of the spliceosomal U4 snRNP core domain and its implication for snRNP biogenesis.
Leung, A.K., Nagai, K., Li, J.(2011) Nature 473: 536-539
- PubMed: 21516107
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09956
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4WZJ - PubMed Abstract:
The spliceosome is a dynamic macromolecular machine that assembles on pre-messenger RNA substrates and catalyses the excision of non-coding intervening sequences (introns). Four of the five major components of the spliceosome, U1, U2, U4 and U5 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs), contain seven Sm proteins (SmB/B', SmD1, SmD2, SmD3, SmE, SmF and SmG) in common. Following export of the U1, U2, U4 and U5 snRNAs to the cytoplasm, the seven Sm proteins, chaperoned by the survival of motor neurons (SMN) complex, assemble around a single-stranded, U-rich sequence called the Sm site in each small nuclear RNA (snRNA), to form the core domain of the respective snRNP particle. Core domain formation is a prerequisite for re-import into the nucleus, where these snRNPs mature via addition of their particle-specific proteins. Here we present a crystal structure of the U4 snRNP core domain at 3.6 Å resolution, detailing how the Sm site heptad (AUUUUUG) binds inside the central hole of the heptameric ring of Sm proteins, interacting one-to-one with SmE-SmG-SmD3-SmB-SmD1-SmD2-SmF. An irregular backbone conformation of the Sm site sequence combined with the asymmetric structure of the heteromeric protein ring allows each base to interact in a distinct manner with four key residues at equivalent positions in the L3 and L5 loops of the Sm fold. A comparison of this structure with the U1 snRNP at 5.5 Å resolution reveals snRNA-dependent structural changes outside the Sm fold, which may facilitate the binding of particle-specific proteins that are crucial to biogenesis of spliceosomal snRNPs.
- MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 0QH, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: