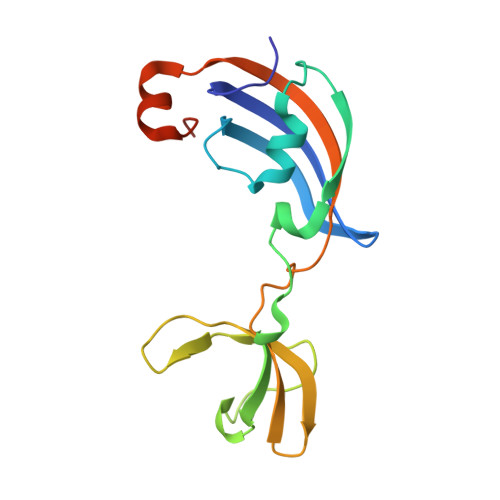
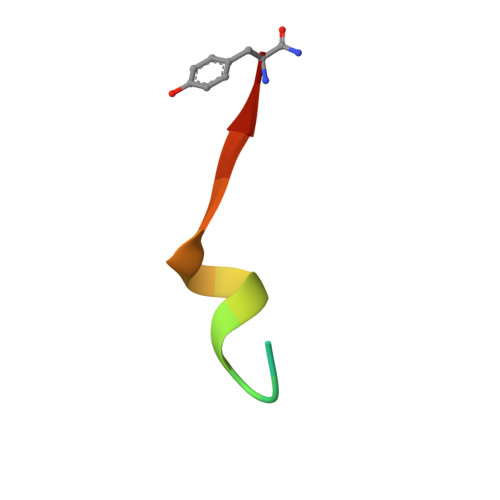
Molecular insights into substrate recognition and catalytic mechanism of the chaperone and FKBP peptidyl-prolyl isomerase SlyD.
Quistgaard, E.M., Weininger, U., Ural-Blimke, Y., Modig, K., Nordlund, P., Akke, M., Low, C.(2016) BMC Biol 14: 82-82
- PubMed: 27664121
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-016-0300-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4ODK, 4ODL, 4ODM, 4ODN, 4ODO, 4ODP, 4ODQ, 4ODR - PubMed Abstract:
Peptidyl-prolyl isomerases (PPIases) catalyze cis/trans isomerization of peptidyl-prolyl bonds, which is often rate-limiting for protein folding. SlyD is a two-domain enzyme containing both a PPIase FK506-binding protein (FKBP) domain and an insert-in-flap (IF) chaperone domain. To date, the interactions of these domains with unfolded proteins have remained rather obscure, with structural information on binding to the FKBP domain being limited to complexes involving various inhibitor compounds or a chemically modified tetrapeptide. We have characterized the binding of 15-residue-long unmodified peptides to SlyD from Thermus thermophilus (TtSlyD) in terms of binding thermodynamics and enzyme kinetics through the use of isothermal titration calorimetry, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, and site-directed mutagenesis. We show that the affinities and enzymatic activity of TtSlyD towards these peptides are much higher than for the chemically modified tetrapeptides that are typically used for activity measurements on FKBPs. In addition, we present a series of crystal structures of TtSlyD with the inhibitor FK506 bound to the FKBP domain, and with 15-residue-long peptides bound to either one or both domains, which reveals that substrates bind in a highly adaptable fashion to the IF domain through β-strand augmentation, and can bind to the FKBP domain as both types VIa1 and VIb-like cis-proline β-turns. Our results furthermore provide important clues to the catalytic mechanism and support the notion of inter-domain cross talk. We found that 15-residue-long unmodified peptides can serve as better substrate mimics for the IF and FKBP domains than chemically modified tetrapeptides. We furthermore show how such peptides are recognized by each of these domains in TtSlyD, and propose a novel general model for the catalytic mechanism of FKBPs that involves C-terminal rotation around the peptidyl-prolyl bond mediated by stabilization of the twisted transition state in the hydrophobic binding site.
- Department of Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics, Karolinska Institutet, Scheeles väg 2, SE-17177, Stockholm, Sweden.
Organizational Affiliation: