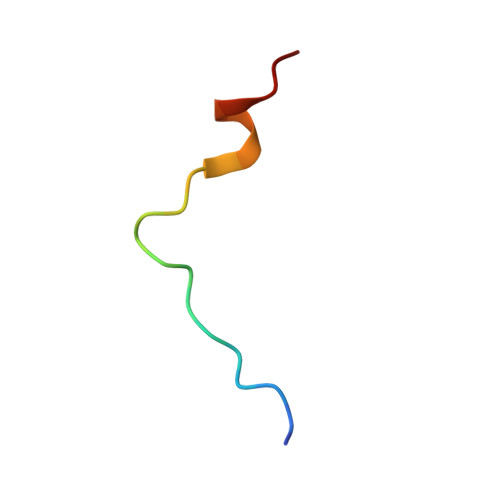
Structure of P15(Paf)-PCNA Complex and Implications for Clamp Sliding During DNA Replication and Repair.
De Biasio, A., De Opakua, A.I., Mortuza, G.B., Molina, R., Cordeiro, T.N., Castillo, F., Villate, M., Merino, N., Delgado, S., Gil-Carton, D., Luque, I., Diercks, T., Bernado, P., Montoya, G., Blanco, F.J.(2015) Nat Commun 6: 6439
- PubMed: 25762514
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms7439
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4D2G - PubMed Abstract:
The intrinsically disordered protein p15(PAF) regulates DNA replication and repair by binding to the proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) sliding clamp. We present the structure of the human p15(PAF)-PCNA complex. Crystallography and NMR show the central PCNA-interacting protein motif (PIP-box) of p15(PAF) tightly bound to the front-face of PCNA. In contrast to other PCNA-interacting proteins, p15(PAF) also contacts the inside of, and passes through, the PCNA ring. The disordered p15(PAF) termini emerge at opposite faces of the ring, but remain protected from 20S proteasomal degradation. Both free and PCNA-bound p15(PAF) binds DNA mainly through its histone-like N-terminal tail, while PCNA does not, and a model of the ternary complex with DNA inside the PCNA ring is consistent with electron micrographs. We propose that p15(PAF) acts as a flexible drag that regulates PCNA sliding along the DNA and facilitates the switch from replicative to translesion synthesis polymerase binding.
- Structural Biology Unit, CIC bioGUNE, Parque Tecnológico de Bizkaia Edificio 800, 48160 Derio, Spain.
Organizational Affiliation: