Structurally Encoded Intraclass Differences in Epha Clusters Drive Distinct Cell Responses
Seiradake, E., Schaupp, A., Del Toro Ruiz, D., Kaufmann, R., Mitakidis, N., Harlos, K., Aricescu, A.R., Klein, R., Jones, E.Y.(2013) Nat Struct Mol Biol 20: 958
- PubMed: 23812375
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2617
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4BK4, 4BK5, 4BKA, 4BKF - PubMed Abstract:
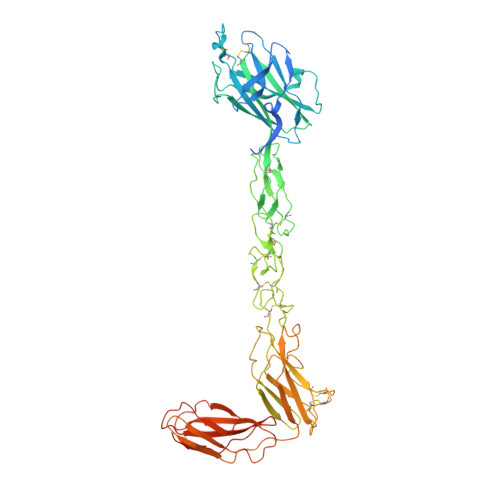
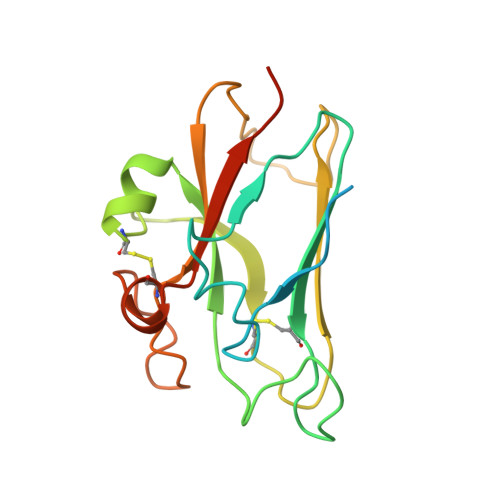
Functional outcomes of ephrin binding to Eph receptors (Ephs) range from cell repulsion to adhesion. Here we used cell collapse and stripe assays, showing contrasting effects of human ephrinA5 binding to EphA2 and EphA4. Despite equivalent ligand binding affinities, EphA4 triggered greater cell collapse, whereas EphA2-expressing cells adhered better to ephrinA5-coated surfaces. Chimeric receptors showed that the ectodomain is a major determinant of cell response. We report crystal structures of EphA4 ectodomain alone and in complexes with ephrinB3 and ephrinA5. These revealed closed clusters with a dimeric or circular arrangement in the crystal lattice, contrasting with extended arrays previously observed for EphA2 ectodomain. Localization microscopy showed that ligand-stimulated EphA4 induces smaller clusters than does EphA2. Mutant Ephs link these characteristics to interactions observed in the crystal lattices, suggesting a mechanism by which distinctive ectodomain surfaces determine clustering, and thereby signaling, properties.
- Division of Structural Biology, Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: