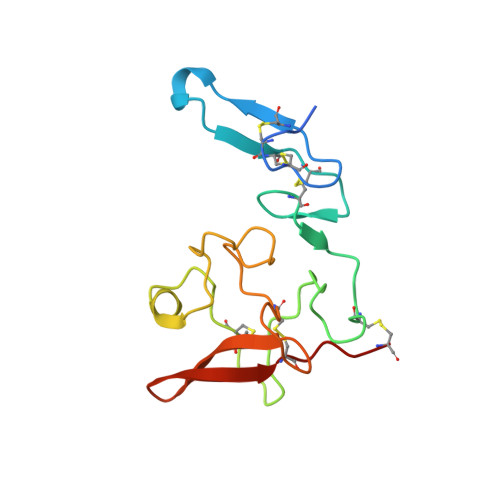
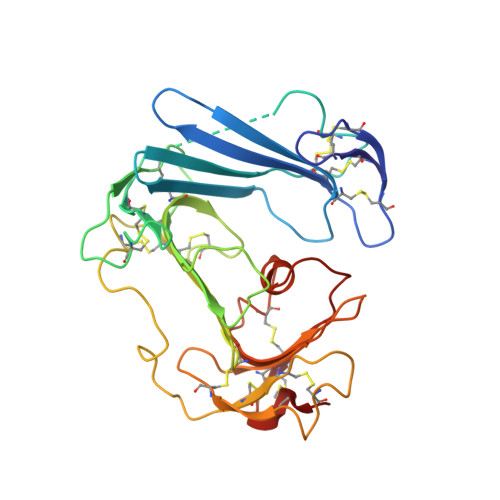
Structure-based engineering of species selectivity in the interaction between urokinase and its receptor: implication for preclinical cancer therapy.
Lin, L., Gardsvoll, H., Huai, Q., Huang, M., Ploug, M.(2010) J Biological Chem 285: 10982-10992
- PubMed: 20133942
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.093492
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3LAQ - PubMed Abstract:
The high affinity interaction between the urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and its glycolipid-anchored receptor (uPAR) is decisive for cell surface-associated plasminogen activation. Because plasmin activity controls fibrinolysis in a variety of pathological conditions, including cancer and wound healing, several intervention studies have focused on targeting the uPA.uPAR interaction in vivo. Evaluations of such studies in xenotransplanted tumor models are, however, complicated by the pronounced species selectivity in this interaction. We now report the molecular basis underlying this difference by solving the crystal structure for the murine uPA.uPAR complex and demonstrate by extensive surface plasmon resonance studies that the kinetic rate constants for this interaction can be swapped completely between these orthologs by exchanging only two residues. This study not only discloses the structural basis required for a successful rational design of the species selectivity in the uPA.uPAR interaction, which is highly relevant for functional studies in mouse models, but it also suggests the possible development of general inhibitors that will target the uPA.uPAR interaction across species barriers.
- Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02215, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: