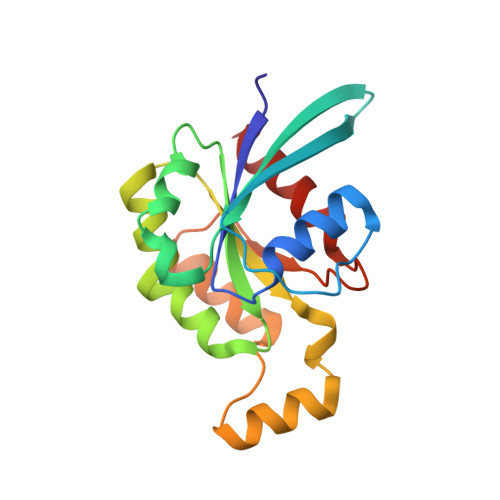
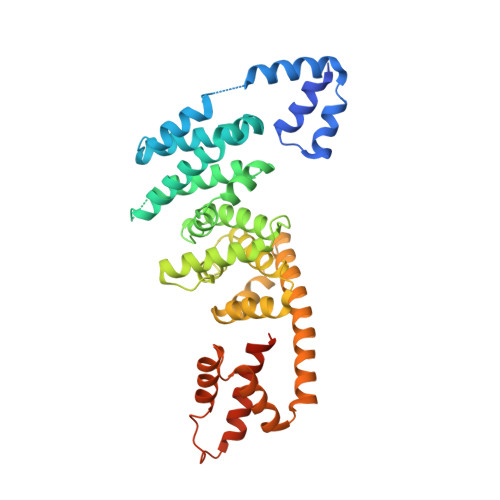
Specificity of Interactions between mDia Isoforms and Rho Proteins
Lammers, M., Meyer, S., Kuhlmann, D., Wittinghofer, A.(2008) J Biological Chem 283: 35236-35246
- PubMed: 18829452
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M805634200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3EG5 - PubMed Abstract:
Formins are key regulators of actin nucleation and polymerization. They contain formin homology 1 (FH1) and 2 (FH2) domains as the catalytic machinery for the formation of linear actin cables. A subclass of formins constitutes the Diaphanous-related formins, members of which are regulated by the binding of a small GTP-binding protein of the Rho subfamily. Binding of these molecular switch proteins to the regulatory N-terminal mDia(N), including the GTPase-binding domain, leads to the release of auto-inhibition. From the three mDia isoforms, mDia1 is activated only by Rho (RhoA, -B, and -C), in contrast to mDia2 and -3, which is also activated by Rac and Cdc42. Little is known about the determinants of specificity. Here we report on the interactions of RhoA, Rac1, and Cdc42 with mDia1 and an mDia1 mutant (mDia(N)-Thr-Ser-His (TSH)), which based on structural information should mimic mDia2 and -3. Specificity is analyzed by biochemical studies and a structural analysis of a complex between Cdc42.Gpp(NH)p and mDia(N)-TSH. A triple NNN motif in mDia1 (amino acids 164-166), corresponding to the TSH motif in mDia2/3 (amino acids 183-185 and 190-192), and the epitope interacting with the Rho insert helix are essential for high affinity binding. The triple N motif of mDia1 allows tight interaction with Rho because of the presence of Phe-106, whereas the corresponding His-104 in Rac and Cdc42 forms a complementary interface with the TSH motif in mDia2/3. We also show that the F106H and H104F mutations drastically alter the affinities and thermodynamics of mDia interactions.
- Max-Planck-Institute for Molecular Physiology, Department of Structural Biology, Otto-Hahn-Strasse 11, 44227 Dortmund, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: