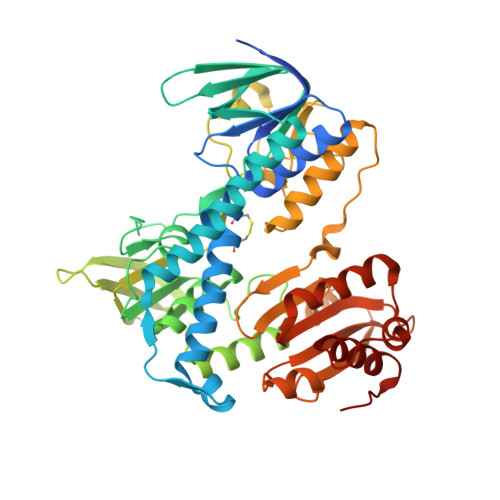
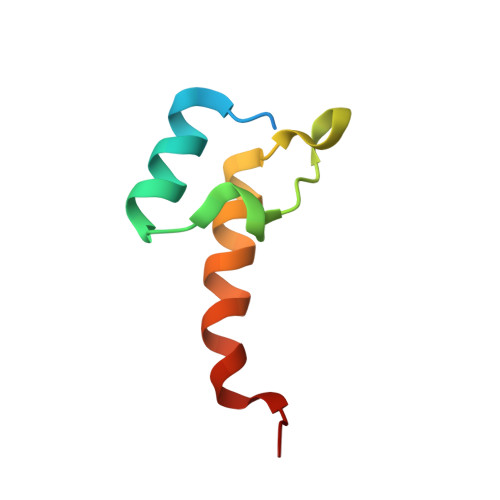
Structural and Thermodynamic Basis for Weak Interactions between Dihydrolipoamide Dehydrogenase and Subunit-binding Domain of the Branched-chain {alpha}-Ketoacid Dehydrogenase Complex.
Brautigam, C.A., Wynn, R.M., Chuang, J.L., Naik, M.T., Young, B.B., Huang, T.H., Chuang, D.T.(2011) J Biological Chem 286: 23476-23488
- PubMed: 21543315
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.202960
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3RNM - PubMed Abstract:
The purified mammalian branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex (BCKDC), which catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of branched-chain α-keto acids, is essentially devoid of the constituent dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase component (E3). The absence of E3 is associated with the low affinity of the subunit-binding domain of human BCKDC (hSBDb) for hE3. In this work, sequence alignments of hSBDb with the E3-binding domain (E3BD) of the mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase complex show that hSBDb has an arginine at position 118, where E3BD features an asparagine. Substitution of Arg-118 with an asparagine increases the binding affinity of the R118N hSBDb variant (designated hSBDb*) for hE3 by nearly 2 orders of magnitude. The enthalpy of the binding reaction changes from endothermic with the wild-type hSBDb to exothermic with the hSBDb* variant. This higher affinity interaction allowed the determination of the crystal structure of the hE3/hSBDb* complex to 2.4-Å resolution. The structure showed that the presence of Arg-118 poses a unique, possibly steric and/or electrostatic incompatibility that could impede E3 interactions with the wild-type hSBDb. Compared with the E3/E3BD structure, the hE3/hSBDb* structure has a smaller interfacial area. Solution NMR data corroborated the interactions of hE3 with Arg-118 and Asn-118 in wild-type hSBDb and mutant hSBDb*, respectively. The NMR results also showed that the interface between hSBDb and hE3 does not change significantly from hSBDb to hSBDb*. Taken together, our results represent a starting point for explaining the long standing enigma that the E2b core of the BCKDC binds E3 far more weakly relative to other α-ketoacid dehydrogenase complexes.
- Department of Biochemistry, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, Texas 75390, USA. chad.brautigam@utsouthwestern.edu
Organizational Affiliation: