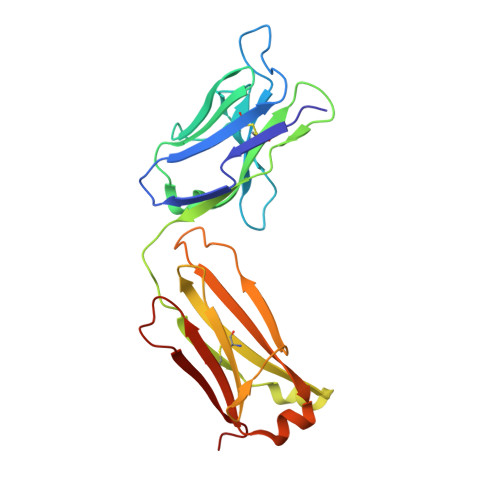
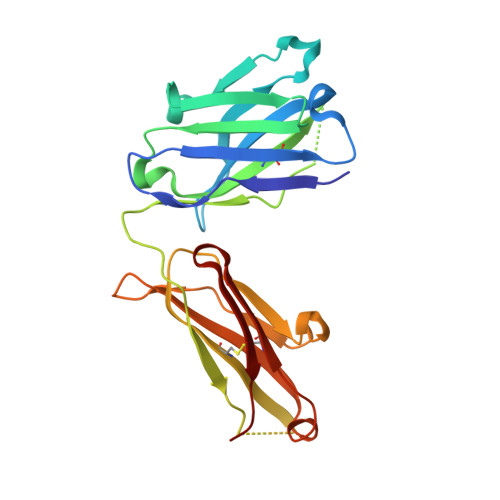
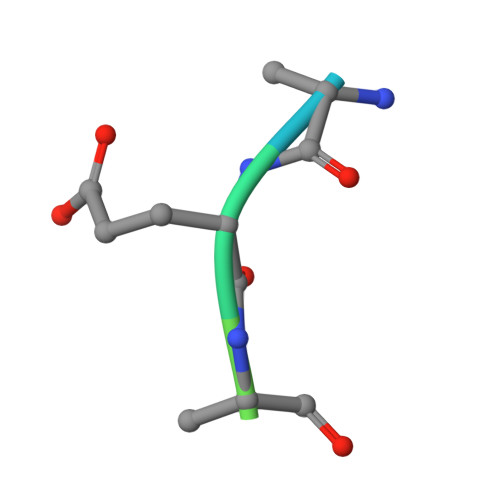
Structure of a human IgA1 Fab fragment at 1.55 angstrom resolution: potential effect of the constant domains on antigen-affinity modulation
Correa, A., Trajtenberg, F., Obal, G., Pritsch, O., Dighiero, G., Oppezzo, P., Buschiazzo, A.(2013) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 69: 388-397
- PubMed: 23519414
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444912048664
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3M8O, 3QNX, 3QNY, 3QNZ, 3QO1 - PubMed Abstract:
Despite being the most abundant class of immunoglobulins in humans and playing central roles in the adaptive immune response, high-resolution structural data are still lacking for the antigen-binding region of human isotype A antibodies (IgAs). The crystal structures of a human Fab fragment of IgA1 in three different crystal forms are now reported. The three-dimensional organization is similar to those of other Fab classes, but FabA1 seems to be more rigid, being constrained by a hydrophobic core in the interface between the variable and constant domains of the heavy chain (VH-CH1) as well as by a disulfide bridge that connects the light and heavy chains, influencing the relative heavy/light-chain orientation. The crystal structure of the same antibody but with a G-isotype CH1 which is reported to display different antigen affinity has also been solved. The differential structural features reveal plausible mechanisms for constant/variable-domain long-distance effects whereby antibody class switching could alter antigen affinity.
- Unit of Recombinant Proteins, Institut Pasteur de Montevideo, 11400 Montevideo, Uruguay.
Organizational Affiliation: