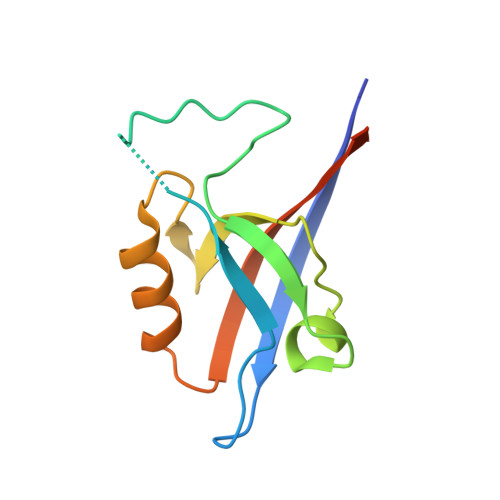
The structural flexibility of the shank1 PDZ domain is important for its binding to different ligands
Lee, J.H., Park, H., Park, S.J., Kim, H.J., Eom, S.H.(2011) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 407: 207-212
- PubMed: 21376703
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.02.141
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3QJM, 3QJN - PubMed Abstract:
The PDZ domain of the shank protein interacts with numerous cell membrane receptors and cytosolic proteins via the loosely defined binding motif X-(Ser/Thr)-X-Φ-COOH (Φ represents hydrophobic residues) at the carboxyl terminus of its target protein. This enables shank to serve as a membrane-associated scaffold for the assembly of signaling complexes. As the list of proteins that bind to the shank PDZ domain grows, it is not immediately clear what structural element(s) mediate this domain's target specificity or the plasticity required to bind its different targets. Here, we have determined the crystal structure of the shank1 PDZ in complex with the βPIX C-terminal pentapeptide (642-646, DETNL) at 2.3Å resolution and modeled shank1 PDZ binding to selected pentapeptide ligands. The resulting structures revealed a large hydrophobic pocket within the PDZ domain that can accommodate a variety of ligand residues at the P(0) position. A H-bond between His735 and Ser/Thr at the P(-2) position is invariant throughout the model structures. In addition, we identified multiple PDZ domain residues that are able to form H-bonds and salt bridges with an incoming target protein. Overall, our study provides a new level of understanding of the specificity and structural plasticity of the shank PDZ domain.
- Korea Polar Research Institute, Incheon 406-840, South Korea. junhyucklee@kopri.re.kr
Organizational Affiliation: