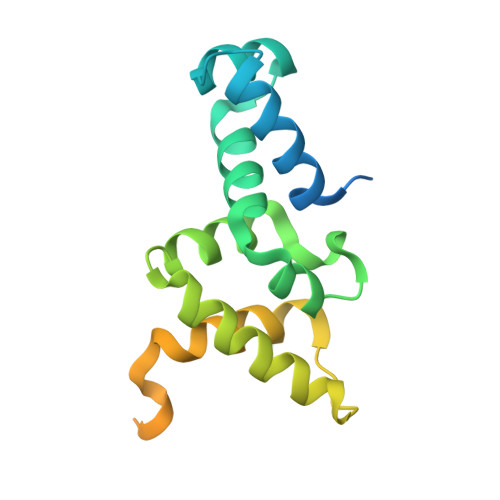
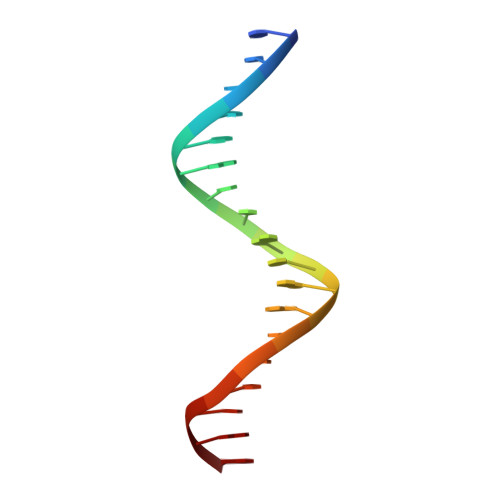
Insight into F plasmid DNA segregation revealed by structures of SopB and SopB-DNA complexes.
Schumacher, M.A., Piro, K.M., Xu, W.(2010) Nucleic Acids Res 38: 4514-4526
- PubMed: 20236989
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq161
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3KZ5, 3MKW, 3MKY, 3MKZ - PubMed Abstract:
Accurate DNA segregation is essential for genome transmission. Segregation of the prototypical F plasmid requires the centromere-binding protein SopB, the NTPase SopA and the sopC centromere. SopB displays an intriguing range of DNA-binding properties essential for partition; it binds sopC to form a partition complex, which recruits SopA, and it also coats DNA to prevent non-specific SopA-DNA interactions, which inhibits SopA polymerization. To understand the myriad functions of SopB, we determined a series of SopB-DNA crystal structures. SopB does not distort its DNA site and our data suggest that SopB-sopC forms an extended rather than wrapped partition complex with the SopA-interacting domains aligned on one face. SopB is a multidomain protein, which like P1 ParB contains an all-helical DNA-binding domain that is flexibly attached to a compact (beta(3)-alpha)(2) dimer-domain. Unlike P1 ParB, the SopB dimer-domain does not bind DNA. Moreover, SopB contains a unique secondary dimerization motif that bridges between DNA duplexes. Both specific and non-specific SopB-DNA bridging structures were observed. This DNA-linking function suggests a novel mechanism for in trans DNA spreading by SopB, explaining how it might mask DNA to prevent DNA-mediated inhibition of SopA polymerization.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Texas, M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Unit 1000, Houston, TX 77030, USA. maschuma@mdanderson.org
Organizational Affiliation: