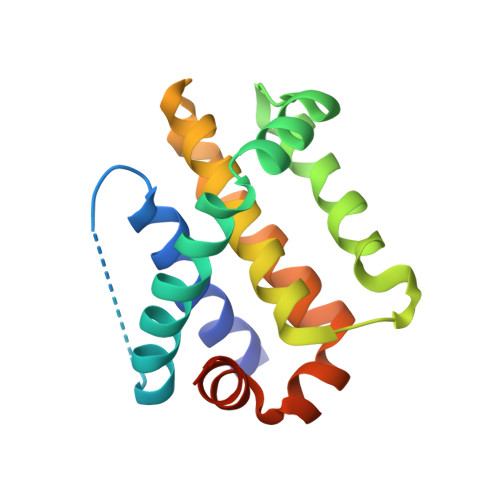
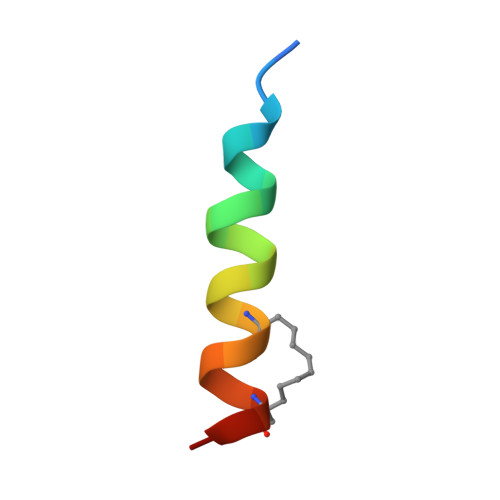
The MCL-1 BH3 helix is an exclusive MCL-1 inhibitor and apoptosis sensitizer.
Stewart, M.L., Fire, E., Keating, A.E., Walensky, L.D.(2010) Nat Chem Biol 6: 595-601
- PubMed: 20562877
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.391
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3MK8 - PubMed Abstract:
The development of selective inhibitors for discrete anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family proteins implicated in pathologic cell survival remains a formidable but pressing challenge. Such precisely tailored compounds would serve as molecular probes and targeted therapies to study and treat human diseases driven by specific anti-apoptotic blockades. In particular, MCL-1 has emerged as a major resistance factor in human cancer. By screening a library of stabilized alpha-helix of BCL-2 domains (SAHBs), we determined that the MCL-1 BH3 helix is itself a potent and exclusive MCL-1 inhibitor. X-ray crystallography and mutagenesis studies defined key binding and specificity determinants, including the capacity to harness the hydrocarbon staple to optimize affinity while preserving selectivity. MCL-1 SAHB directly targets MCL-1, neutralizes its inhibitory interaction with pro-apoptotic BAK and sensitizes cancer cells to caspase-dependent apoptosis. By leveraging nature's solution to ligand selectivity, we generated an MCL-1-specific agent that defines the structural and functional features of targeted MCL-1 inhibition.
- Department of Pediatric Oncology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Children's Hospital Boston, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: