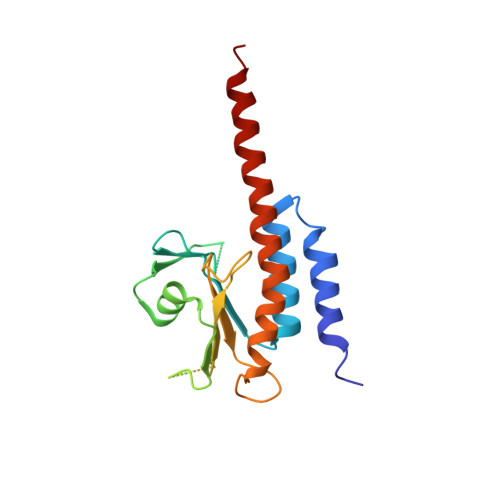
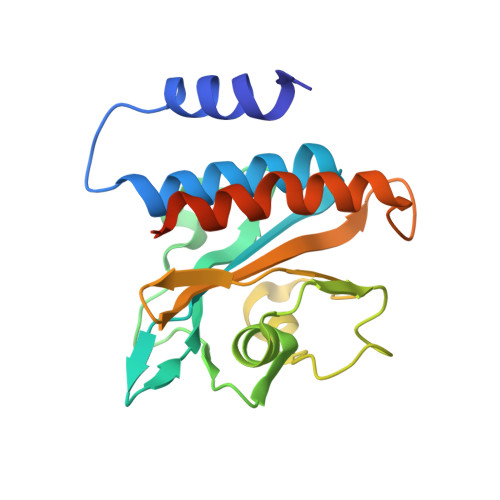
Domain Organization and Conformational Plasticity of the G Protein Effector, PDE6.
Zhang, Z., He, F., Constantine, R., Baker, M.L., Baehr, W., Schmid, M.F., Wensel, T.G., Agosto, M.A.(2015) J Biological Chem 290: 12833-12843
- PubMed: 25809480
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.647636
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3JAB, 3JBQ - PubMed Abstract:
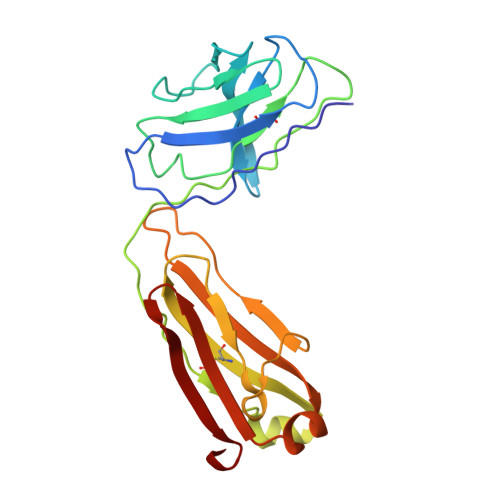
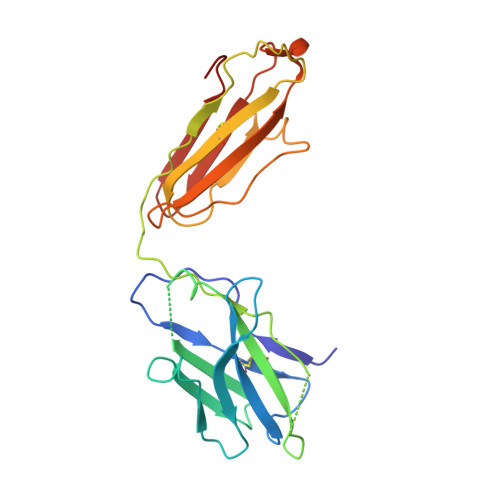
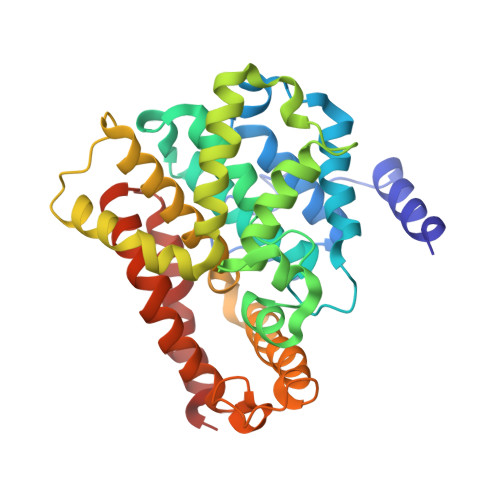
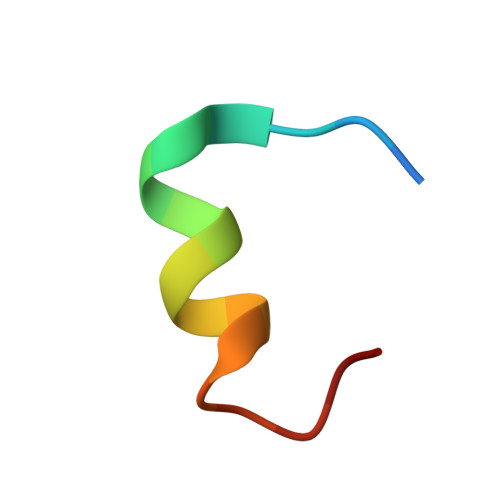
The cGMP phosphodiesterase of rod photoreceptor cells, PDE6, is the key effector enzyme in phototransduction. Two large catalytic subunits, PDE6α and -β, each contain one catalytic domain and two non-catalytic GAF domains, whereas two small inhibitory PDE6γ subunits allow tight regulation by the G protein transducin. The structure of holo-PDE6 in complex with the ROS-1 antibody Fab fragment was determined by cryo-electron microscopy. The ∼11 Å map revealed previously unseen features of PDE6, and each domain was readily fit with high resolution structures. A structure of PDE6 in complex with prenyl-binding protein (PrBP/δ) indicated the location of the PDE6 C-terminal prenylations. Reconstructions of complexes with Fab fragments bound to N or C termini of PDE6γ revealed that PDE6γ stretches from the catalytic domain at one end of the holoenzyme to the GAF-A domain at the other. Removal of PDE6γ caused dramatic structural rearrangements, which were reversed upon its restoration.
- From the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas 77030 and.
Organizational Affiliation: