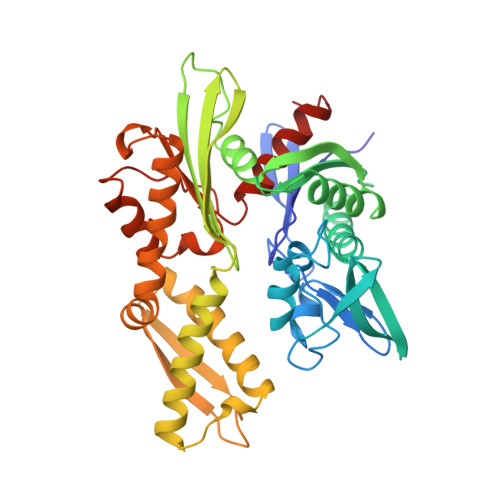
Three-dimensional structure of the ATPase fragment of a 70K heat-shock cognate protein.
Flaherty, K.M., DeLuca-Flaherty, C., McKay, D.B.(1990) Nature 346: 623-628
- PubMed: 2143562
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/346623a0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3HSC - PubMed Abstract:
The three-dimensional structure of the amino-terminal 44K ATPase fragment of the 70K bovine heat-shock cognate protein has been solved to a resolution of 2.2 A. The ATPase fragment has two structural lobes with a deep cleft between them; ATP binds at the base of the cleft. Surprisingly, the nucleotide-binding 'core' of the ATPase fragment has a tertiary structure similar to that of hexokinase, although the remainder of the structures of the two proteins are completely dissimilar, suggesting that both the phosphotransferase mechanism and the substrate-induced conformational change intrinsic to the hexokinases may be used by the 70K heat shock-related proteins.
- Beckman Laboratories for Structural Biology, Department of Cell Biology, Stanford University School of Medicine, California 94305-5400.
Organizational Affiliation: