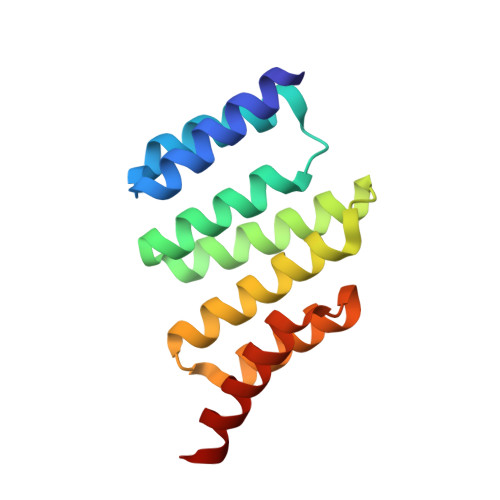
Redesign of a protein-peptide interaction: characterization and applications
Jackrel, M.E., Valverde, R., Regan, L.(2009) Protein Sci 18: 762-774
- PubMed: 19309728
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.75
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3FWV - PubMed Abstract:
The design of protein-peptide interactions has a wide array of practical applications and also reveals insight into the basis for molecular recognition. Here, we present the redesign of a tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) protein scaffold, along with its corresponding peptide ligand. We show that the binding properties of these protein-peptide pairs can be understood, quantitatively, using straightforward chemical considerations. The recognition pairs we have developed are also practically useful for the specific identification of tagged proteins. We demonstrate the facile replacement of these proteins, which we have termed T-Mods (TPR-based recognition module), for antibodies in both detection and purification applications. The new protein-peptide pair has a dissociation constant that is weaker than typical antibody-antigen interactions, yet the recognition pair is highly specific and we have shown that this affinity is sufficient for both Western blotting and affinity purification. Moreover, we demonstrate that this more moderate affinity is actually advantageous for purification applications, because extremely harsh conditions are not required to dissociate the T-Mod-peptide interaction. The results we present are important, not only because they represent a successful application of protein design but also because they help define the properties that should be sought in other scaffolds that are being developed as antibody replacements.
- Department of Chemistry, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut 06520, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: