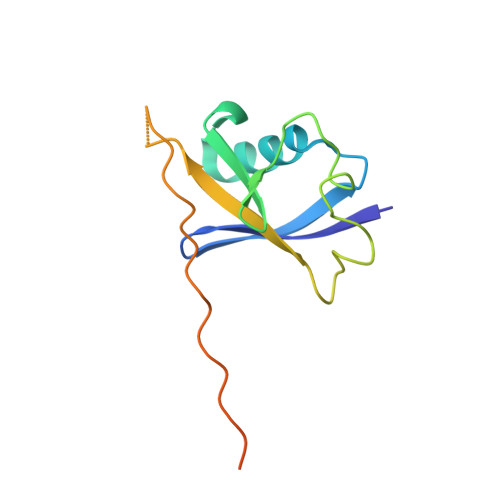
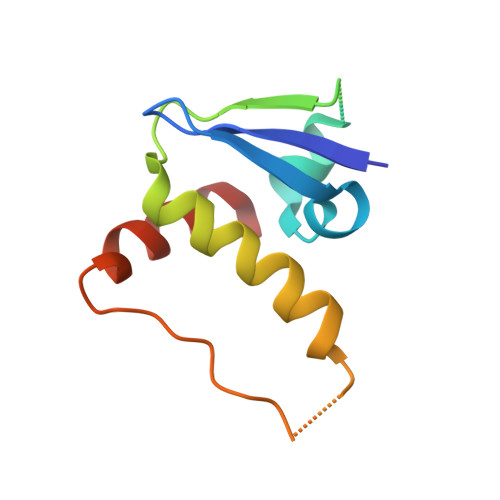
Structural insight into the human immunodeficiency virus Vif SOCS box and its role in human E3 ubiquitin ligase assembly
Stanley, B.J., Ehrlich, E.S., Short, L., Yu, Y., Xiao, Z., Yu, X.-F., Xiong, Y.(2008) J Virol 82: 8656-8663
- PubMed: 18562529
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00767-08
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3DCG - PubMed Abstract:
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) virion infectivity factor (Vif) causes the proteasome-mediated destruction of human antiviral protein APOBEC3G by tethering it to a cellular E3 ubiquitin ligase composed of ElonginB, ElonginC, Cullin5, and Rbx2. It has been proposed that HIV Vif hijacks the E3 ligase through two regions within its C-terminal domain: a BC box region that interacts with ElonginC and a novel zinc finger motif that interacts with Cullin5. We have determined the crystal structure of the HIV Vif BC box in complex with human ElonginB and ElonginC. This complex presents direct structural evidence of the recruitment of a human ubiquitin ligase by a viral BC box protein that mimics the conserved interactions of cellular ubiquitin ligases. We further mutated conserved hydrophobic residues in a region downstream of the Vif BC box. These mutations demonstrate that this region, the Vif Cullin box, composes a third E3-ligase recruiting site critical for interaction between Vif and Cullin5. Furthermore, our homology modeling reveals that the Vif Cullin box and zinc finger motif may be positioned adjacent to the N terminus of Cullin5 for interaction with loop regions in the first cullin repeat of Cullin5.
- Department of Molecular Biophysics and Biochemistry, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut 06510, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: