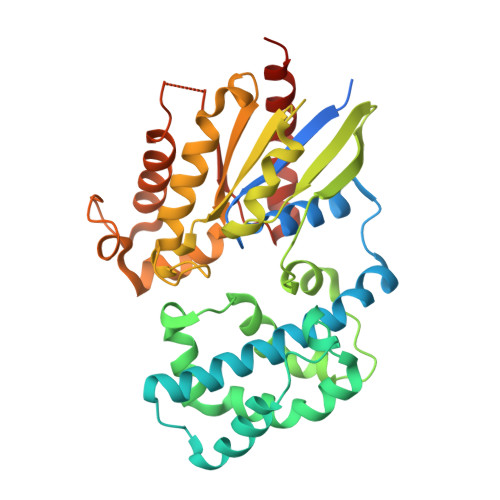
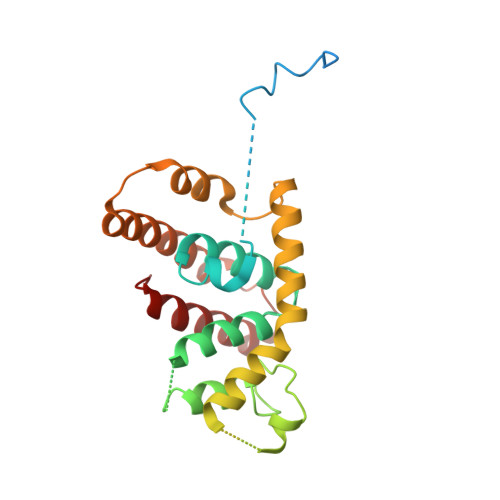
Identification of critical residues in G(alpha)13 for stimulation of p115RhoGEF activity and the structure of the G(alpha)13-p115RhoGEF regulator of G protein signaling homology (RH) domain complex.
Hajicek, N., Kukimoto-Niino, M., Mishima-Tsumagari, C., Chow, C.R., Shirouzu, M., Terada, T., Patel, M., Yokoyama, S., Kozasa, T.(2011) J Biological Chem 286: 20625-20636
- PubMed: 21507947
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.201392
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3AB3 - PubMed Abstract:
RH-RhoGEFs are a family of guanine nucleotide exchange factors that contain a regulator of G protein signaling homology (RH) domain. The heterotrimeric G protein Gα(13) stimulates the guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) activity of RH-RhoGEFs, leading to activation of RhoA. The mechanism by which Gα(13) stimulates the GEF activity of RH-RhoGEFs, such as p115RhoGEF, has not yet been fully elucidated. Here, specific residues in Gα(13) that mediate activation of p115RhoGEF are identified. Mutation of these residues significantly impairs binding of Gα(13) to p115RhoGEF as well as stimulation of GEF activity. These data suggest that the exchange activity of p115RhoGEF is stimulated allosterically by Gα(13) and not through its interaction with a secondary binding site. A crystal structure of Gα(13) bound to the RH domain of p115RhoGEF is also presented, which differs from a previously crystallized complex with a Gα(13)-Gα(i1) chimera. Taken together, these data provide new insight into the mechanism by which p115RhoGEF is activated by Gα(13).
- Department of Pharmacology, College of Medicine, University of Illinois, Chicago, Illinois 60612, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: