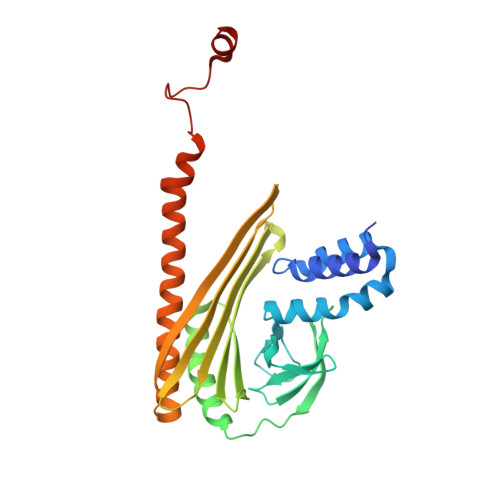
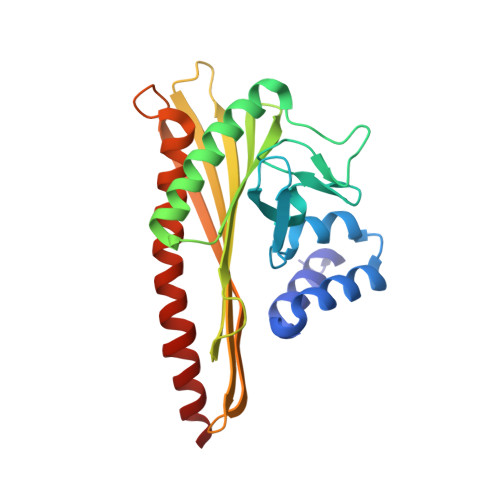
Two distinct mechanisms for actin capping protein regulation--steric and allosteric inhibition
Takeda, S., Minakata, S., Koike, R., Kawahata, I., Narita, A., Kitazawa, M., Ota, M., Yamakuni, T., Maeda, Y., Nitanai, Y.(2010) PLoS Biol 8: e1000416-e1000416
- PubMed: 20625546
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1000416
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3AA0, 3AA1, 3AA6, 3AA7, 3AAA - PubMed Abstract:
The actin capping protein (CP) tightly binds to the barbed end of actin filaments, thus playing a key role in actin-based lamellipodial dynamics. V-1 and CARMIL proteins directly bind to CP and inhibit the filament capping activity of CP. V-1 completely inhibits CP from interacting with the barbed end, whereas CARMIL proteins act on the barbed end-bound CP and facilitate its dissociation from the filament (called uncapping activity). Previous studies have revealed the striking functional differences between the two regulators. However, the molecular mechanisms describing how these proteins inhibit CP remains poorly understood. Here we present the crystal structures of CP complexed with V-1 and with peptides derived from the CP-binding motif of CARMIL proteins (CARMIL, CD2AP, and CKIP-1). V-1 directly interacts with the primary actin binding surface of CP, the C-terminal region of the alpha-subunit. Unexpectedly, the structures clearly revealed the conformational flexibility of CP, which can be attributed to a twisting movement between the two domains. CARMIL peptides in an extended conformation interact simultaneously with the two CP domains. In contrast to V-1, the peptides do not directly compete with the barbed end for the binding surface on CP. Biochemical assays revealed that the peptides suppress the interaction between CP and V-1, despite the two inhibitors not competing for the same binding site on CP. Furthermore, a computational analysis using the elastic network model indicates that the interaction of the peptides alters the intrinsic fluctuations of CP. Our results demonstrate that V-1 completely sequesters CP from the barbed end by simple steric hindrance. By contrast, CARMIL proteins allosterically inhibit CP, which appears to be a prerequisite for the uncapping activity. Our data suggest that CARMIL proteins down-regulate CP by affecting its conformational dynamics. This conceptually new mechanism of CP inhibition provides a structural basis for the regulation of the barbed end elongation in cells.
- Structural Biology Research Center, Graduate School of Science, Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan. takeda.shuichi@f.mbox.nagoya-u.ac.jp
Organizational Affiliation: