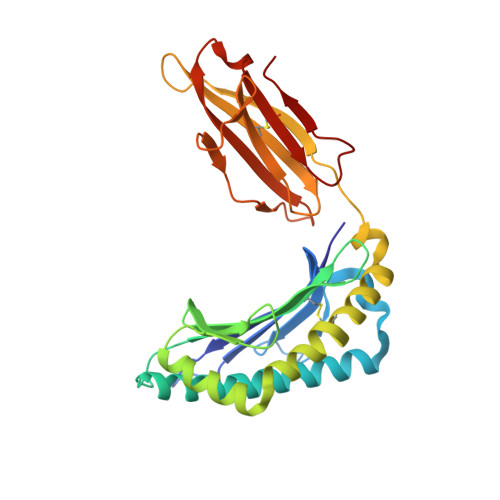
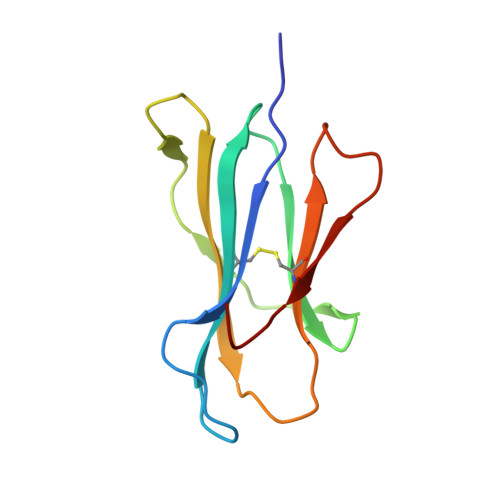
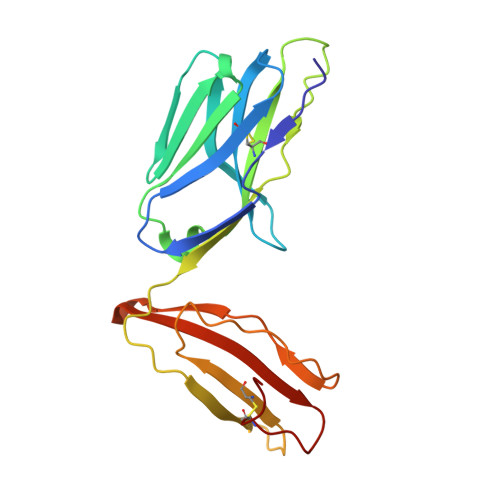
Directed evolution of human T cell receptor CDR2 residues by phage display dramatically enhances affinity for cognate peptide-MHC without increasing apparent cross-reactivity.
Dunn, S.M., Rizkallah, P.J., Baston, E., Mahon, T., Cameron, B., Moysey, R., Gao, F., Sami, M., Boulter, J., Li, Y., Jakobsen, B.K.(2006) Protein Sci 15: 710-721
- PubMed: 16600963
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.051936406
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2F53, 2F54 - PubMed Abstract:
The mammalian alpha/beta T cell receptor (TCR) repertoire plays a pivotal role in adaptive immunity by recognizing short, processed, peptide antigens bound in the context of a highly diverse family of cell-surface major histocompatibility complexes (pMHCs). Despite the extensive TCR-MHC interaction surface, peptide-independent cross-reactivity of native TCRs is generally avoided through cell-mediated selection of molecules with low inherent affinity for MHC. Here we show that, contrary to expectations, the germ line-encoded complementarity determining regions (CDRs) of human TCRs, namely the CDR2s, which appear to contact only the MHC surface and not the bound peptide, can be engineered to yield soluble low nanomolar affinity ligands that retain a surprisingly high degree of specificity for the cognate pMHC target. Structural investigation of one such CDR2 mutant implicates shape complementarity of the mutant CDR2 contact interfaces as being a key determinant of the increased affinity. Our results suggest that manipulation of germ line CDR2 loops may provide a useful route to the production of high-affinity TCRs with therapeutic and diagnostic potential.
- Avidex Limited, Abingdon, Oxon, OX14 4RX, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: