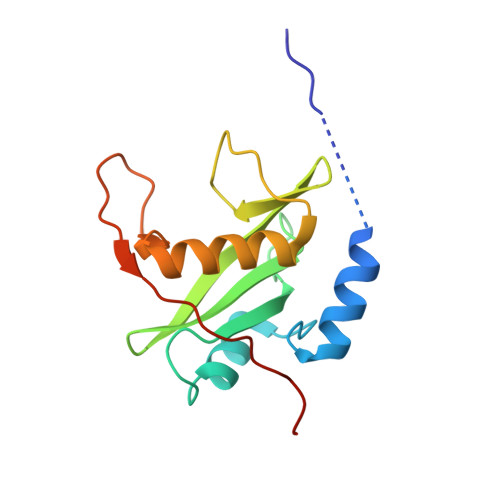
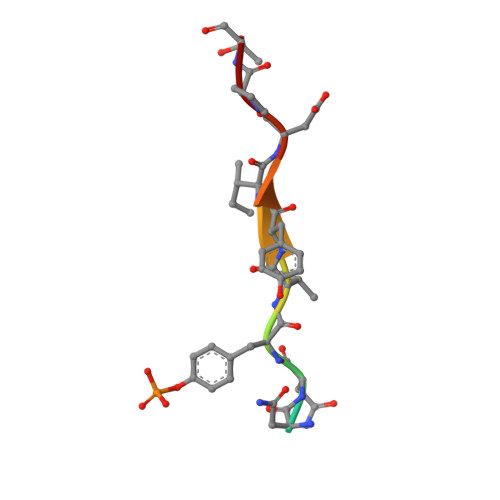
Structural Basis for C-Kit Inhibition by the Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 6 (Socs6) Ubiquitin Ligase.
Zadjali, F., Pike, A.C.W., Vesterlund, M., Sun, J., Wu, C., Li, S.S., Ronnstrand, L., Knapp, S., Bullock, A., Flores-Morales, A.(2011) J Biological Chem 286: 480
- PubMed: 21030588
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.173526
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2VIF - PubMed Abstract:
The c-KIT receptor tyrosine kinase mediates the cellular response to stem cell factor (SCF). Whereas c-KIT activity is important for the proliferation of hematopoietic cells, melanocytes and germ cells, uncontrolled c-KIT activity contributes to the growth of diverse human tumors. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 6 (SOCS6) is a member of the SOCS family of E3 ubiquitin ligases that can interact with c-KIT and suppress c-KIT-dependent pathways. Here, we analyzed the molecular mechanisms that determine SOCS6 substrate recognition. Our results show that the SH2 domain of SOCS6 is essential for its interaction with c-KIT pY568. The 1.45-Å crystal structure of SOCS6 SH2 domain bound to the c-KIT substrate peptide (c-KIT residues 564-574) revealed a highly complementary and specific interface giving rise to a high affinity interaction (K(d) = 0.3 μm). Interestingly, the SH2 binding pocket extends to substrate residue position pY+6 and envelopes the c-KIT phosphopeptide with a large BG loop insertion that contributes significantly to substrate interaction. We demonstrate that SOCS6 has ubiquitin ligase activity toward c-KIT and regulates c-KIT protein turnover in cells. Our data support a role of SOCS6 as a feedback inhibitor of SCF-dependent signaling and provides molecular data to account for target specificity within the SOCS family of ubiquitin ligases.
- Department of Molecular Medicine and Surgery, Karolinska Institutet, SE-17177 Stockholm, Sweden.
Organizational Affiliation: