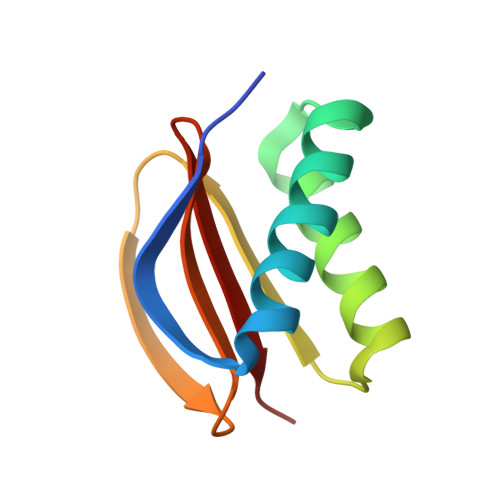
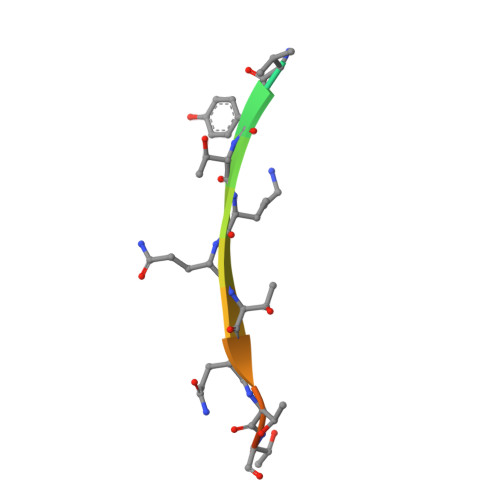
Structure and dynamics of LC8 complexes with KXTQT-motif peptides: swallow and dynein intermediate chain compete for a common site.
Benison, G., Karplus, P.A., Barbar, E.(2007) J Mol Biology 371: 457-468
- PubMed: 17570393
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2007.05.046
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2P2T - PubMed Abstract:
The dynein light chain LC8 is an integral subunit of the cytoplasmic dynein motor complex that binds directly to and promotes assembly of the dynein intermediate chain (IC). LC8 interacts also with a variety of putative dynein cargo molecules such as Bim, a proapoptotic Bcl2 family protein, which have the KXTQT recognition sequence and neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), which has the GIQVD fingerprint but shares the same binding grooves at the LC8 dimer interface. The work reported here investigates the interaction of LC8 with IC and a putative cargo, Swallow, which share the KXTQT recognition sequence, and addresses the apparent paradox of how LC8, as part of dynein, mediates binding to cargo. The structures of Drosophila LC8 bound to peptides from IC and Swallow solved by X-ray diffraction show that the IC and Swallow peptides bind in the same grooves at the dimer interface. Differences in flexibility between bound and free LC8 were evaluated from hydrogen isotope exchange experiments using heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy. Peptide binding causes an increase in protection from exchange primarily in residues that interact directly with the peptide, such as the beta-strand intertwined at the interface and the N-terminal end of helix alpha2. There is considerably more protection upon Swallow binding, consistent with tighter binding relative to IC. Comparison with the LC8/nNOS complex shows how both the GIQVD and KXTQT fingerprints are recognized in the same groove. The similar structures of LC8/IC and LC8/Swa and the tighter binding of Swallow call into question the role for LC8 as a cargo adaptor protein, and suggest that binding of LC8 to Swallow serves another function, possibly that of a dimerization engine, which is independent of its role in dynein.
- Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR 97331, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: