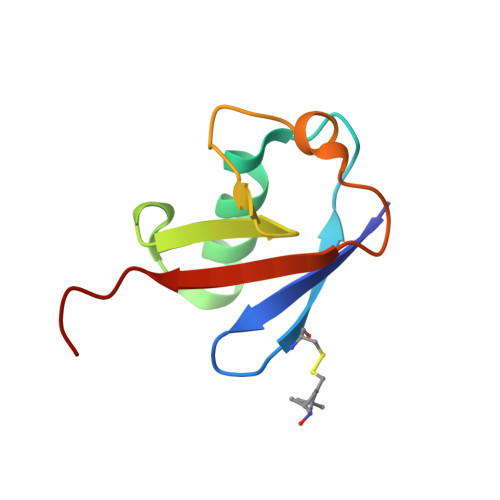
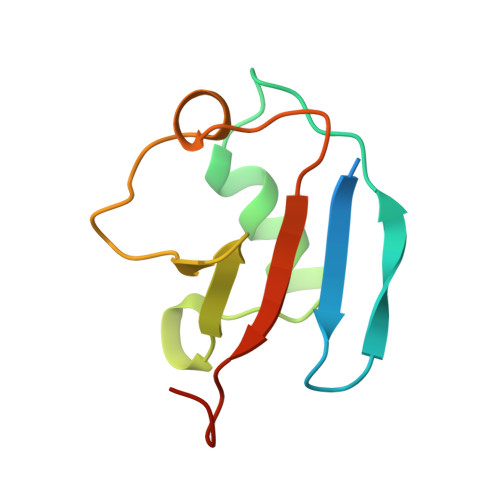
DNA-Damage-Inducible 1 Protein (Ddi1) Contains an Uncharacteristic Ubiquitin-like Domain that Binds Ubiquitin.
Nowicka, U., Zhang, D., Walker, O., Krutauz, D., Castaneda, C.A., Chaturvedi, A., Chen, T.Y., Reis, N., Glickman, M.H., Fushman, D.(2015) Structure 23: 542-557
- PubMed: 25703377
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2015.01.010
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2MR9, 2MRO, 2MRP, 2MWS - PubMed Abstract:
Ddi1 belongs to a family of shuttle proteins targeting polyubiquitinated substrates for proteasomal degradation. Unlike the other proteasomal shuttles, Rad23 and Dsk2, Ddi1 remains an enigma: its function is not fully understood and structural properties are poorly characterized. We determined the structure and binding properties of the ubiquitin-like (UBL) and ubiquitin-associated (UBA) domains of Ddi1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. We found that while Ddi1UBA forms a characteristic UBA:ubiquitin complex, Ddi1UBL has entirely uncharacteristic binding preferences. Despite having a ubiquitin-like fold, Ddi1UBL does not interact with typical UBL receptors but unexpectedly binds ubiquitin, forming a unique interface mediated by hydrophobic contacts and by salt bridges between oppositely charged residues of Ddi1UBL and ubiquitin. In stark contrast to ubiquitin and other UBLs, the β-sheet surface of Ddi1UBL is negatively charged and therefore is recognized in a completely different way. The dual functionality of Ddi1UBL, capable of binding both ubiquitin and proteasome, suggests an intriguing mechanism for Ddi1 as a proteasomal shuttle.
- Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Center for Biomolecular Structure and Organization, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 20742, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: