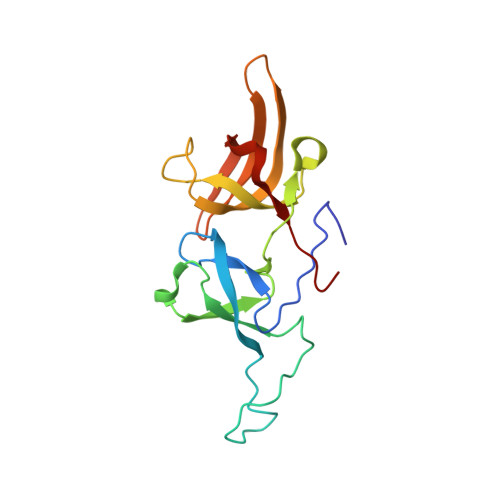
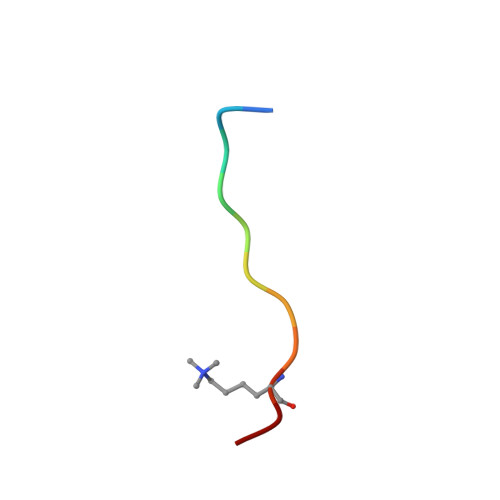
Recognition of Multivalent Histone States Associated with Heterochromatin by UHRF1 Protein.
Nady, N., Lemak, A., Walker, J.R., Avvakumov, G.V., Kareta, M.S., Achour, M., Xue, S., Duan, S., Allali-Hassani, A., Zuo, X., Wang, Y.X., Bronner, C., Chedin, F., Arrowsmith, C.H., Dhe-Paganon, S.(2011) J Biological Chem 286: 24300-24311
- PubMed: 21489993
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.234104
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2L3R, 3DB3, 3DB4 - PubMed Abstract:
Histone modifications and DNA methylation represent two layers of heritable epigenetic information that regulate eukaryotic chromatin structure and gene activity. UHRF1 is a unique factor that bridges these two layers; it is required for maintenance DNA methylation at hemimethylated CpG sites, which are specifically recognized through its SRA domain and also interacts with histone H3 trimethylated on lysine 9 (H3K9me3) in an unspecified manner. Here we show that UHRF1 contains a tandem Tudor domain (TTD) that recognizes H3 tail peptides with the heterochromatin-associated modification state of trimethylated lysine 9 and unmodified lysine 4 (H3K4me0/K9me3). Solution NMR and crystallographic data reveal the TTD simultaneously recognizes H3K9me3 through a conserved aromatic cage in the first Tudor subdomain and unmodified H3K4 within a groove between the tandem subdomains. The subdomains undergo a conformational adjustment upon peptide binding, distinct from previously reported mechanisms for dual histone mark recognition. Mutant UHRF1 protein deficient for H3K4me0/K9me3 binding shows altered localization to heterochromatic chromocenters and fails to reduce expression of a target gene, p16(INK4A), when overexpressed. Our results demonstrate a novel recognition mechanism for the combinatorial readout of histone modification states associated with gene silencing and add to the growing evidence for coordination of, and cross-talk between, the modification states of H3K4 and H3K9 in regulation of gene expression.
- Ontario Cancer Institute, and Department of Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario M5G 1L7, Canada.
Organizational Affiliation: