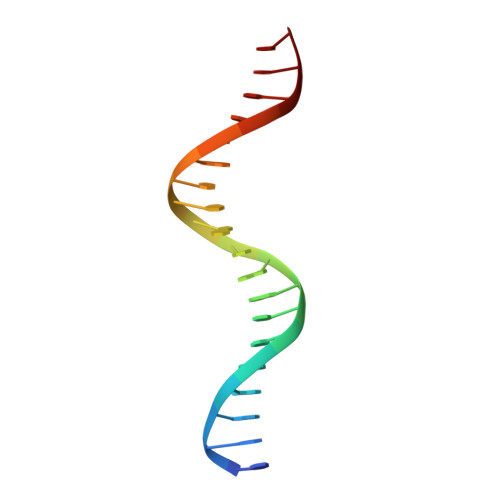
Crystal structure of a bZIP/DNA complex at 2.2 A: determinants of DNA specific recognition.
Keller, W., Konig, P., Richmond, T.J.(1995) J Mol Biology 254: 657-667
- PubMed: 7500340
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1995.0645
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2DGC - PubMed Abstract:
The X-ray structure of the GCN4-bZIP protein bound to DNA containing the ATF/CREB recognition sequence has been refined at 2.2 A. The water-mediated interactions between the basic domain and DNA are revealed, and combined with a more accurate description of the direct contacts, further clarify how binding specificity is achieved. Water molecules extend the interactions of both invariant basic domain residues, asparagine 235 and arginine 243, beyond their direct base contacts. The slight bending of the basic domain alpha-helix around the DNA facilitates the linking of arginine 241, 243 and 245 to main-chain carbonyl oxygen atoms via water molecules, apparently stabilizing interactions with the DNA.
- Institut für Molekularbiologie und Biophysik, ETH-Hönggerberg, Zurich, Switzerland.
Organizational Affiliation: