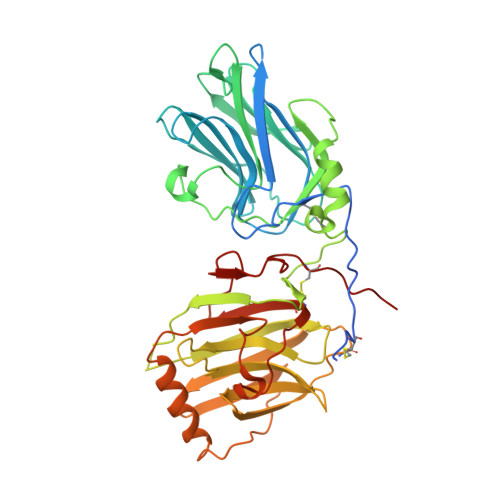
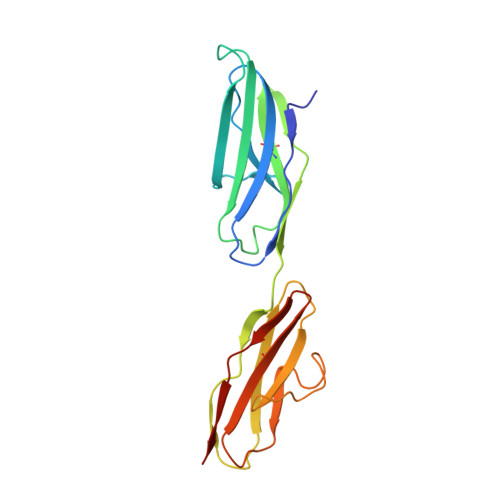
Structural Basis for Gas6-Axl Signalling.
Sasaki, T., Knyazev, P.G., Clout, N.J., Cheburkin, Y., Goehring, W., Ullrich, A., Timpl, R., Hohenester, E.(2006) EMBO J 25: 80
- PubMed: 16362042
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600912
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2C5D - PubMed Abstract:
Receptor tyrosine kinases of the Axl family are activated by the vitamin K-dependent protein Gas6. Axl signalling plays important roles in cancer, spermatogenesis, immunity, and platelet function. The crystal structure at 3.3 A resolution of a minimal human Gas6/Axl complex reveals an assembly of 2:2 stoichiometry, in which the two immunoglobulin-like domains of the Axl ectodomain are crosslinked by the first laminin G-like domain of Gas6, with no direct Axl/Axl or Gas6/Gas6 contacts. There are two distinct Gas6/Axl contacts of very different size, both featuring interactions between edge beta-strands. Structure-based mutagenesis, protein binding assays and receptor activation experiments demonstrate that both the major and minor Gas6 binding sites are required for productive transmembrane signalling. Gas6-mediated Axl dimerisation is likely to occur in two steps, with a high-affinity 1:1 Gas6/Axl complex forming first. Only the minor Gas6 binding site is highly conserved in the other Axl family receptors, Sky/Tyro3 and Mer. Specificity at the major contact is suggested to result from the segregation of charged and apolar residues to opposite faces of the newly formed beta-sheet.
- Max-Planck-Institut für Biochemie, Martinsried, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: