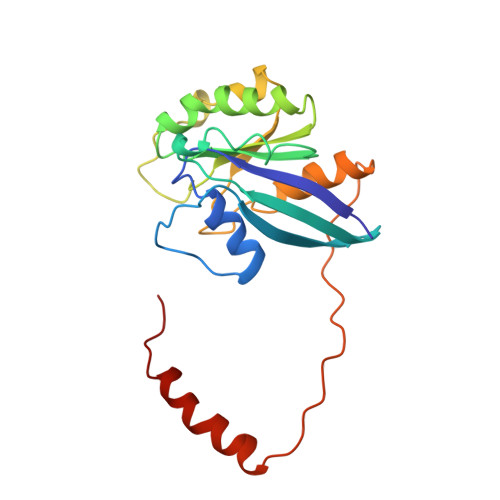
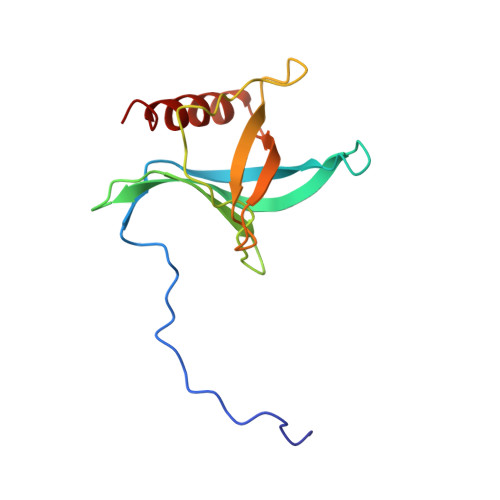
Structure of a Ran-binding domain complexed with Ran bound to a GTP analogue: implications for nuclear transport.
Vetter, I.R., Nowak, C., Nishimoto, T., Kuhlmann, J., Wittinghofer, A.(1999) Nature 398: 39-46
- PubMed: 10078529
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/17969
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1RRP - PubMed Abstract:
The protein Ran is a small GTP-binding protein that binds to two types of effector inside the cell: Ran-binding proteins, which have a role in terminating export processes from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, and importin-beta-like molecules that bind cargo proteins during nuclear transport. The Ran-binding domain is a conserved sequence motif found in several proteins that participate in these transport processes. The Ran-binding protein RanBP2 contains four of these domains and constitutes a large part of the cytoplasmic fibrils that extend from the nuclear-pore complex. The structure of Ran bound to a non-hydrolysable GTP analogue (Ran x GppNHp) in complex with the first Ran-binding domain (RanBD1) of human RanBP2 reveals not only that RanBD1 has a pleckstrin-homology domain fold, but also that the switch-I region of Ran x GppNHp resembles the canonical Ras GppNHp structure and that the carboxy terminus of Ran is wrapped around RanBD1, contacting a basic patch on RanBD1 through its acidic end. This molecular 'embrace' enables RanBDs to sequester the Ran carboxy terminus, triggering the dissociation of Ran x GTP from importin-beta-related transport factors and facilitating GTP hydrolysis by the GTPase-activating protein ranGAP. Such a mechanism represents a new type of switch mechanism and regulatory protein-protein interaction for a Ras-related protein.
- Abteilung Strukturelle Biologie, Max-Planck-Institut für molekulare Physiologie, Dortmund, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: