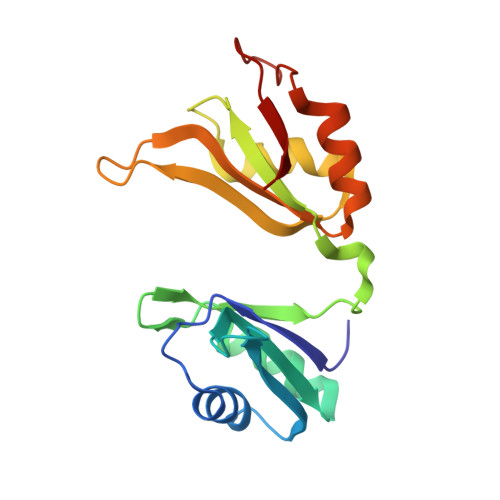
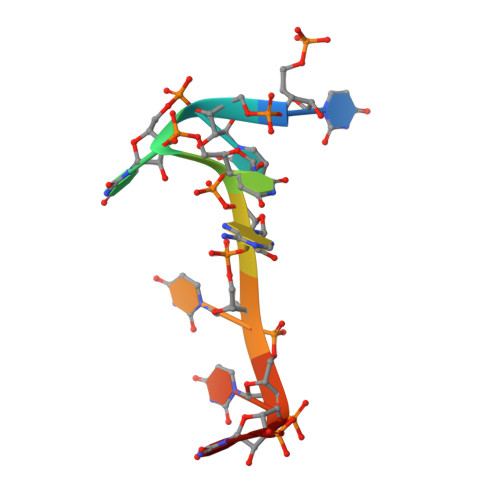
Structural basis for recognition of AU-rich element RNA by the HuD protein.
Wang, X., Tanaka Hall, T.M.(2001) Nat Struct Biol 8: 141-145
- PubMed: 11175903
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/84131
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1FXL, 1G2E - PubMed Abstract:
Hu proteins bind to adenosine-uridine (AU)-rich elements (AREs) in the 3' untranslated regions of many short-lived mRNAs, thereby stabilizing them. Here we report the crystal structures of the first two RNA recognition motif (RRM) domains of the HuD protein in complex with an 11-nucleotide fragment of a class I ARE (the c-fos ARE; to 1.8 A), and with an 11-nucleotide fragment of a class II ARE (the tumor necrosis factor alpha ARE; to 2.3 A). These structures reveal a consensus RNA recognition sequence that suggests a preference for pyrimidine-rich sequences and a requirement for a central uracil residue in the clustered AUUUA repeats found in class II AREs. Comparison to structures of other RRM domain-nucleic acid complexes reveals two base recognition pockets in all the structures that interact with bases using residues in conserved ribonucleoprotein motifs and at the C-terminal ends of RRM domains. Different conformations of nucleic acid can be bound by RRM domains by using different combinations of base recognition pockets and multiple RRM domains.
- Laboratory of Structural Biology, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Institutes of Health, Research Triangle Park, North Carolina 27709, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: