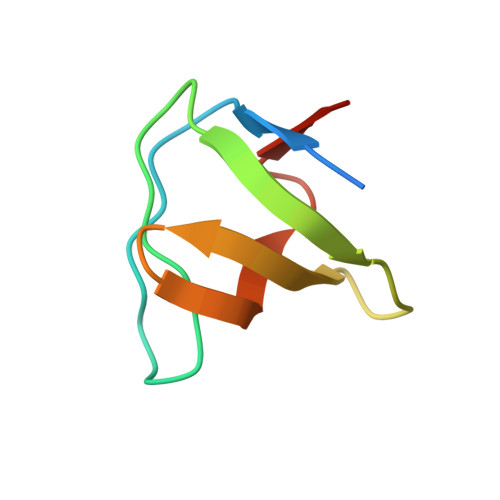
Structural Basis for Recognition of the T Cell Adaptor Protein SLP-76 by the SH3 Domain of Phospholipase Cgamma1
Deng, L., Velikovsky, C.A., Swaminathan, C.P., Cho, S., Mariuzza, R.A.(2005) J Mol Biology 352: 1-10
- PubMed: 16061254
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2005.06.072
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1YWO, 1YWP - PubMed Abstract:
The enzyme phospholipase Cgamma1 (PLCgamma1) is essential for T cell signaling and activation. Following T cell receptor ligation, PLCgamma1 interacts through its SH2 and SH3 domains with the adaptors LAT and SLP-76, respectively, to form a multiprotein signaling complex that leads to activation of PLCgamma1 by Syk tyrosine kinases. To identify the binding site for PLCgamma1 in SLP-76, we used isothermal titration calorimetry to measure affinities for the interaction of PLCgamma1-SH3 with a set of overlapping peptides spanning the central proline-rich region of SLP-76. PLCgamma1-SH3 bound with high specificity to the SLP-76 motif 186PPVPPQRP193, which represents the minimal binding site. To understand the basis for selective recognition, we determined the crystal structures of PLCgamma1-SH3 in free form, and bound to a 10-mer peptide containing this site, to resolutions of 1.60 A and 1.81 A, respectively. The structures reveal that several key contacting residues of the SH3 shift toward the SLP-76 peptide upon complex formation, optimizing the fit and strengthening hydrophobic interactions. Selectivity results mainly from strict shape complementarity between protein and peptide, rather than sequence-specific hydrogen bonding. In addition, Pro193 of SLP-76 assists in positioning Arg192 into the compass pocket of PLCgamma1-SH3, which coordinates the compass residue through an unusual aspartate. The PLCgamma1-SH3/SLP-76 structure provides insights into ligand binding by SH3 domains related to PLCgamma1-SH3, as well as into recognition by PLCgamma1 of signaling partners other than SLP-76.
- Center for Advanced Research in Biotechnology, W. M. Keck Laboratory for Structural Biology, University of Maryland Biotechnology Institute, Rockville, MD 20850, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: