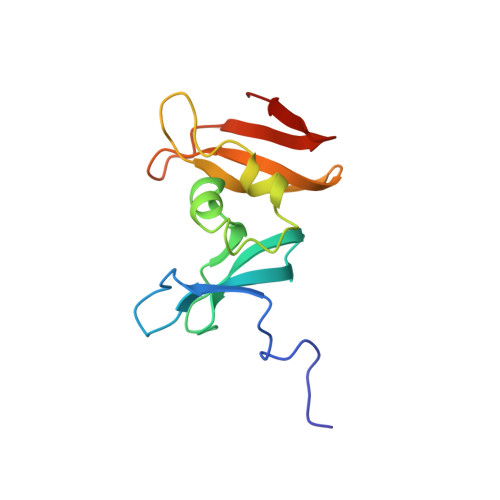
Solution structure of the C-terminal single-stranded DNA-binding domain of Escherichia coli topoisomerase I.
Yu, L., Zhu, C.X., Tse-Dinh, Y.C., Fesik, S.W.(1995) Biochemistry 34: 7622-7628
- PubMed: 7779808
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00023a008
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1YUA - PubMed Abstract:
Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I catalyzes the interconversion of different topological forms of DNA. In this paper we describe NMR studies of a 14K C-terminal fragment of this enzyme that binds preferentially to single-stranded DNA and enhances the enzyme's ability to relax negatively supercoiled DNA under high salt conditions. The 1H, 13C, and 15N resonances of the protein were assigned from a number of heteronuclear multidimensional NMR experiments, and the three-dimensional structure of the protein was determined from a total of 2188 NMR-derived restraints. The root-mean-square deviation about the mean coordinate positions for residues 13-120 is 0.68 +/- 0.11 A for the backbone atoms and 1.09 +/- 0.09 A for all heavy atoms. The overall fold, which consists of two four-stranded beta-sheets separated by two helices, differs from other DNA- and RNA-binding proteins such as gene 5, cold shock protein, and hnRNP C. From an analysis of the changes in chemical shift upon the addition of single-stranded DNA, the location of the oligonucleotide binding site was determined. The binding site consists of a beta-sheet containing positively charged and aromatic amino acids and, in spite of its different structure, is similar to that found in other proteins that bind single-stranded oligonucleotides.
- NMR Research, D-47G, AP10, Abbott Laboratories, Illinois 60064, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: