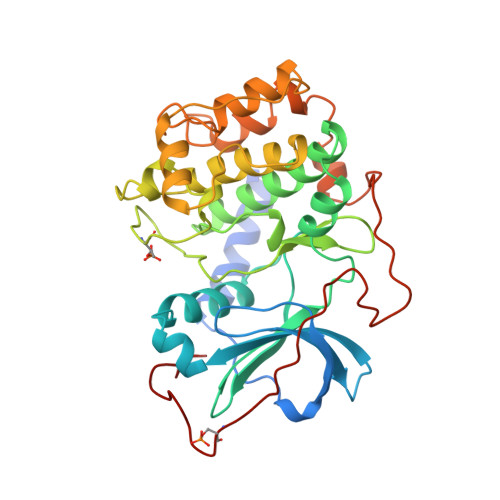
Crystal structures of catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase in complex with isoquinolinesulfonyl protein kinase inhibitors H7, H8, and H89. Structural implications for selectivity.
Engh, R.A., Girod, A., Kinzel, V., Huber, R., Bossemeyer, D.(1996) J Biological Chem 271: 26157-26164
- PubMed: 8824261
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.271.42.26157
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1YDR, 1YDS, 1YDT - PubMed Abstract:
The discovery of several hundred different protein kinases involved in highly diverse cellular signaling pathways is in stark contrast to the much smaller number of known modulators of cell signaling. Of these, the H series protein kinase inhibitors (1-(5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)-2-methylpiperazine (H7), N-[2-(methylamino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide (H8) N-[2-(p-Bromocinnamylamino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide (H89)) are frequently used to block signaling pathways in studies of cellular regulation. To elucidate inhibition mechanisms at atomic resolution and to enable structure-based drug design of potential therapeutic modulators of signaling pathways, we determined the crystal structures of corresponding complexes with the cAPK catalytic subunit. Complexes with H7 and H8 (2.2 A) and with H89 (2.3 A) define the binding mode of the isoquinoline-sulfonamide derivatives in the ATP-binding site while demonstrating effects of ligand-induced structural change. Specific interactions between the enzyme and the inhibitors include the isoquinoline ring nitrogen ligating to backbone amide of Val-123 and an inhibitor side chain amide bonding to the backbone carbonyl of Glu-170. The conservation of the ATP-binding site of protein kinases allows evaluation of factors governing general selectivity of these inhibitors among kinases. These results should assist efforts in the design of protein kinase inhibitors with specific properties.
- Abteilung Strukturforschung II, Max-Planck Institute for Biochemistry, D-82152 Martinsried, Federal Republic of Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: