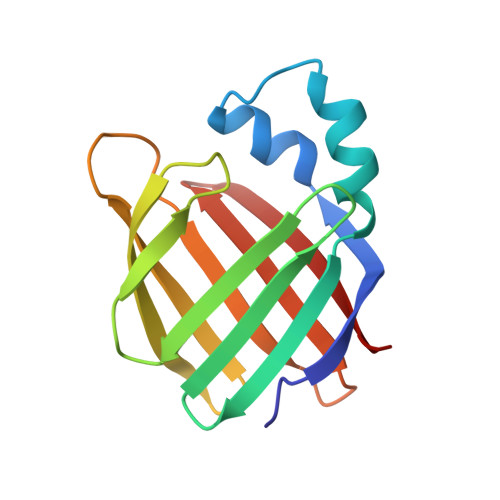
Crystal structure of apo-cellular retinoic acid-binding protein type II (R111M) suggests a mechanism of ligand entry.
Chen, X., Tordova, M., Gilliland, G.L., Wang, L., Li, Y., Yan, H., Ji, X.(1998) J Mol Biology 278: 641-653
- PubMed: 9600845
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1998.1734
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1XCA - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of unliganded mutant R111M of human cellular retinoic acid-binding protein type II (apo-CRABPII (R111M)) has been determined at 2.3 A and refined to a crystallographic R-factor of 0. 18. Although the mutant protein has lower affinity for all-trans-retinoic acid (RA) than the wild-type, it is properly folded, and its conformation is very similar to the wild-type. apo-CRABPII (R111M) crystallizes in space group P1 with two molecules in the unit cell. The two molecules have high structural similarity except that their alpha2 helices differ strikingly. Analyses of the molecular conformation and crystal packing environment suggest that one of the two molecules assumes a conformation compatible with RA entry. Three structural elements encompassing the opening of the binding pocket exhibit large conformational changes, when compared with holo-CRABPII, which include the alpha2 helix and the betaC-betaD and betaE-betaF hairpin loops. The alpha2 helix is unwound at its N terminus, which appears to be essential for the opening of the RA-binding pocket. Three arginine side-chains (29, 59, and 132) are found with their guanidino groups pointing into the RA-binding pocket. A three-step mechanism of RA entry has been proposed, addressing the opening of the RA entrance, the electrostatic potential that directs entry of RA into the binding pocket, and the intramolecular interactions that stabilize the RA.CRABPII complex via locking the three flexible structural elements when RA is bound.
- ABL-Basic Research Program, National Cancer Institute-Frederick Cancer Research and Development Center, Frederick, MD 21702, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: