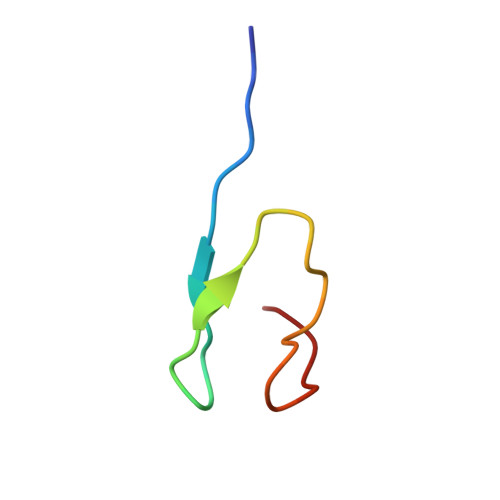
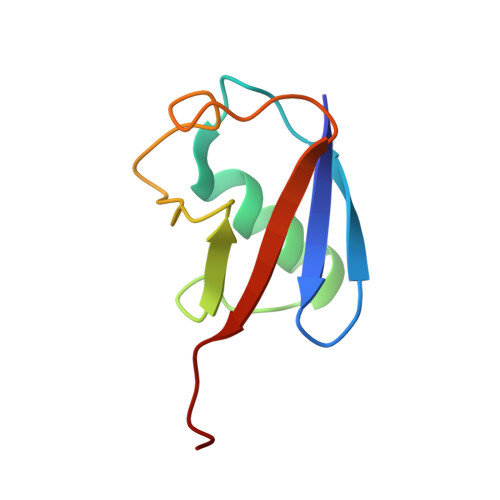
Ubiquitin interactions of NZF zinc fingers.
Alam, S.L., Sun, J., Payne, M., Welch, B.D., Blake, B.K., Davis, D.R., Meyer, H.H., Emr, S.D., Sundquist, W.I.(2004) EMBO J 23: 1411-1421
- PubMed: 15029239
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600114
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1Q5W - PubMed Abstract:
Ubiquitin (Ub) functions in many different biological pathways, where it typically interacts with proteins that contain modular Ub recognition domains. One such recognition domain is the Npl4 zinc finger (NZF), a compact zinc-binding module found in many proteins that function in Ub-dependent processes. We now report the solution structure of the NZF domain from Npl4 in complex with Ub. The structure reveals that three key NZF residues (13TF14/M25) surrounding the zinc coordination site bind the hydrophobic 'Ile44' surface of Ub. Mutations in the 13TF14/M25 motif inhibit Ub binding, and naturally occurring NZF domains that lack the motif do not bind Ub. However, substitution of the 13TF14/M25 motif into the nonbinding NZF domain from RanBP2 creates Ub-binding activity, demonstrating the versatility of the NZF scaffold. Finally, NZF mutations that inhibit Ub binding by the NZF domain of Vps36/ESCRT-II also inhibit sorting of ubiquitylated proteins into the yeast vacuole. Thus, the NZF is a versatile protein recognition domain that is used to bind ubiquitylated proteins during vacuolar protein sorting, and probably many other biological processes.
- Department of Biochemistry, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, USA. alam@wsu.edu
Organizational Affiliation: