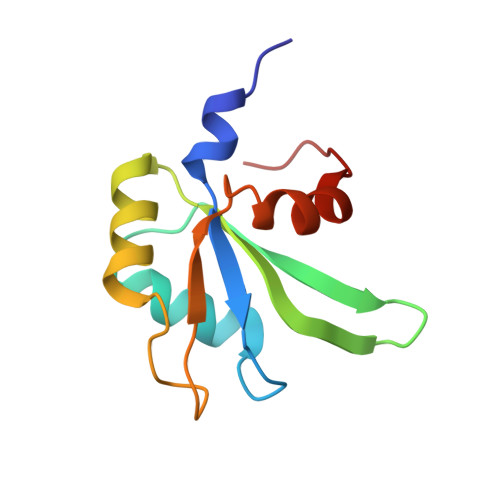
Recognition of GU-rich polyadenylation regulatory elements by human CstF-64 protein
Perez-Canadillas, J.M., Varani, G.(2003) EMBO J 22: 2821-2830
- PubMed: 12773396
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/cdg259
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1P1T - PubMed Abstract:
Vertebrate polyadenylation sites are identified by the AAUAAA signal and by GU-rich sequences downstream of the cleavage site. These are recognized by a heterotrimeric protein complex (CstF) through its 64 kDa subunit (CstF-64); the strength of this interaction affects the efficiency of poly(A) site utilization. We present the structure of the RNA-binding domain of CstF-64 containing an RNA recognition motif (RRM) augmented by N- and C-terminal helices. The C-terminal helix unfolds upon RNA binding and extends into the hinge domain where interactions with factors responsible for assembly of the polyadenylation complex occur. We propose that this conformational change initiates assembly. Consecutive Us are required for a strong CstF-GU interaction and we show how UU dinucleotides are recognized. Contacts outside the UU pocket fine tune the protein-RNA interaction and provide different affinities for distinct GU-rich elements. The protein-RNA interface remains mobile, most likely a requirement to bind many GU-rich sequences and yet discriminate against other RNAs. The structural distinction between sequences that form stable and unstable complexes provides an operational distinction between weakly and strongly processed poly(A) sites.
- MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 2QH, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: